Is Center of Mass Useful?
A square wire of side length and mass is centered on the origin in the plane. A point-particle of mass is positioned at .
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the two objects?
Details and assumptions:
1)
Everything in standard physical units
2)
Gravitational constant
3)
4)
5)
The wire's mass is uniformly distributed over its length
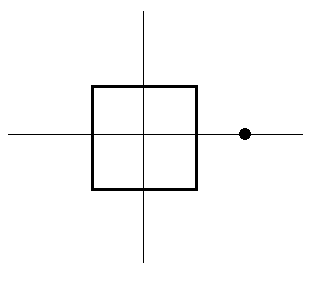
The answer is 80.267.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 G M 2 ( ∫ − 1 / 2 1 / 2 ( 1 / 4 + y 2 ) 3 / 2 1 / 2 d y + ∫ − 1 / 2 1 / 2 ( 9 / 4 + y 2 ) 3 / 2 1 / 2 d y + 2 ∫ − 1 / 2 1 / 2 ( 1 / 4 + ( 1 − x ) 2 ) 3 / 2 1 − x d x ) = 6 6 . 7 ( 2 − 3 1 0 2 ) ≈ 8 0 . 2 6 6
With the dimensions of the wire being large relative to the distance of the attracting bodies, naively using the center of mass does not give a good approximation, of course.