Is it easy?
Consider the equation n x 4 + 4 x + 3 = 0 . The number of positive integers n such that the above equation has a real root is A and sum of all such values of n is S . Find the value of A + S .
This is the part of the set Polynomialism .
The answer is 2.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Complete your explanation
Log in to reply
Sorry, there was a problem. Is there a problem with brilliant? I can't load the pages properly! Edit, Post and Preview buttons doesn't work!
Now good explanation!!
Isn't it supposed to be y=nx^4 + 4x + 3?
Check that x = 0 is not a solution. n x 4 + 4 x + 3 = 0 n = x 4 − 4 x − 3 ≥ 1 (Because n is a positive integer) x 4 + 4 x + 3 ≤ 0 ( x 2 − 1 ) 2 + 2 ( x + 1 ) 2 ≤ 0
So x = − 1 is the unique solution which occurs when equality above holds i.e. n = 1 is the only positive integer.
A = 1 and S = 1
A + S = 1 + 1 = 2
Moderator note:
How can one approach this problem without first guessing that the answer is 1? IE Your solution heavily relied on ( n − 1 ) x 4 + ( x 4 + 4 x + 3 ) ≥ 0 , so what's the motivation for that?
Simple motivation: Working backwards in this solution lead to this question
Slightly Differently
L e t x = y − 1 d o m a i n o f y i s ( − ∞ , ∞ ) − { 0 } n = − x 3 4 − x 4 3 = 4 y 3 − 3 y 4 = f ( y ) d y d n = 1 2 y 2 ( 1 − y ) s o n = f ( y ) i n c r e a s i n g f o r y < 1 & d e c r e a s i n g f o r y > 1 ⇒ n m a x = f ( 1 ) = 1 s o o n l y o n e + v e i n t e g e r p o s s i b l e . A + S = 1 + 1 = 2
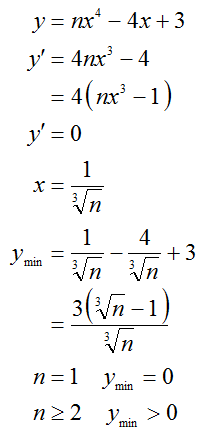
I want to use a little bit calculus here. Let f ( x ) = n x 4 and g ( x ) = − 4 x − 3 . We want f ( x ) = g ( x ) has one real solution at least. Note that as n grows graph of f ( x ) = n x 4 becomes narrower and it will not touch the g ( x ) after some n = n 0 . So boundary is where f ( x ) is tangent to g ( x ) at some point x = a and n = n 0 , in other words where f ( a ) = g ( a ) and f ′ ( a ) = g ′ ( a ) or n 0 a 4 = − 4 a − 3 4 n 0 a 3 = − 4 which gives a = − 1 and n 0 = 1 . Therefore n ≤ n 0 = 1 .