Is it hard?
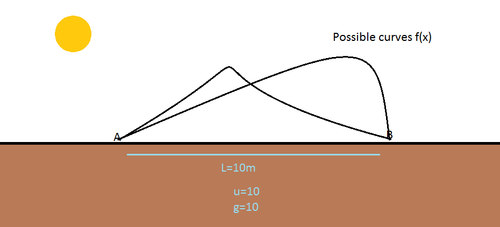 Consider all the possible continuous smooth 2-D curves joining two points on the
ground
( 'A' and 'B' ) seperatedd by a distance
L
and lying
entirely
in the vertical plane,
Consider all the possible continuous smooth 2-D curves joining two points on the
ground
( 'A' and 'B' ) seperatedd by a distance
L
and lying
entirely
in the vertical plane,
Let the curve be described as
y=f(x)
satisfying
f'(0)=1
and also as has been mentioned f(0)=f(L)
A particle is to be launched along the curve with an initial speed of u from A, so as to reach at B,
What is the equation of the curve f(x) so that the curve exerts absolutely no Normal reaction upon the particle at each and every point on the curve,
if it can be expressed as
Find the sum of the coefficients (algebraic sum , not sum of magnitudes)
Details and Assumptions
1) L= 10
2) g= 10
3) u= 10
3) Neglect buoyancy , viscous drag , size of particle and variation of 'g' with height
(ALL IN SI UNITS)
The answer is 0.9.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
This question is just too easy since normal at any point is zero hence we can expect the ball to follow it's normal trajectory that is the trajectory of a normal projectile, that is projectile of a parabola.
Hence I would just be writing the equation of trajectory :
y = x t a n ( θ ) − 2 u 2 c o s 2 ( θ ) g x 2
Put the values to get :
y = x − 1 0 x 2