Is this defined?
Given A = x 2 + 1 0 x + 2 5 x . Find the maximum value of A .( x is a real number)
If the answer is in the form of b a where a , b are coprime positive integers, type a + b .
Bonus: What is the value of x so that A achieves its maximum value?
The answer is 21.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
This problem is in the realm of calculus.
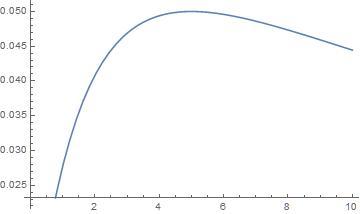
The maximum occurs at a value of x where the value of first derivative of the function x → ( x + 5 ) 2 x is 0 .
∂ x ∂ ( x + 5 ) 2 x ⇒ ( x + 5 ) 2 1 − ( x + 5 ) 3 2 x
( x + 5 ) 2 1 − ( x + 5 ) 3 2 x ⇒ ( x + 5 ) − 2 x = 0 ⇒ x = 5
∂ x ∂ x ∂ 2 ( x + 5 ) 2 x ⇒ ( x + 5 ) 4 6 x − ( x + 5 ) 3 4 evaluated at x = 5 is − 1 0 0 0 1 , of which the important fact is that the value is negative and therefore the extrema is a maximum. If it were positive, then it would be a minimum. If zero, then is would be a "saddle", a level spot in the function.
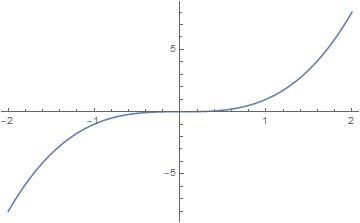
To illustration the last point, x → x 3 :
∂ x ∂ x 3 ⇒ 3 x 2 . That equation has a double root at x = 0 . ∂ x ∂ x ∂ 2 x 3 ⇒ 6 x evaluated at x = 0 is also 0 . This indicates a level spot.
A= p 1 , where p=x+10+ x 2 5 .
Minimum value of x+ x 2 5 is 10 (A.M.-G.M. inequality). So the minimum value of p is 20. Therefore the maximum value of A is 2 0 1 when x=5