Is WolframAlpha powerful enough?
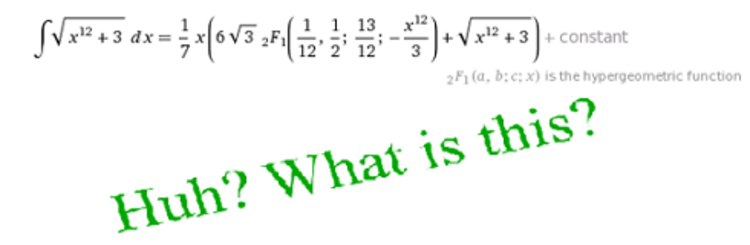
Can the integral above be expressed in terms of elementary functions alone?
Details and Assumptions :
- You may want to read up what elementary functions are.
No copyright infringement intended.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Refer to Integrals of differential binomials and Chebyshev's criterion .
Let y = x 6 , then the integral becomes 6 1 ∫ y − 4 / 5 ( 3 + y 2 ) 1 / 2 d y which is in the form of F ( x ) = ∫ x m ( a + b x n ) p d x where m = − 5 4 , a = 3 , b = 1 , n = 2 , p = 2 1 .
It can be evaluated in terms of elementary functions if and only if at one of the numbers p , n m + 1 , n m + 1 + p is an integer. By inspection, none of these are integers. Hence, it can't be integrated in terms of elementary functions alone.