It Golden!
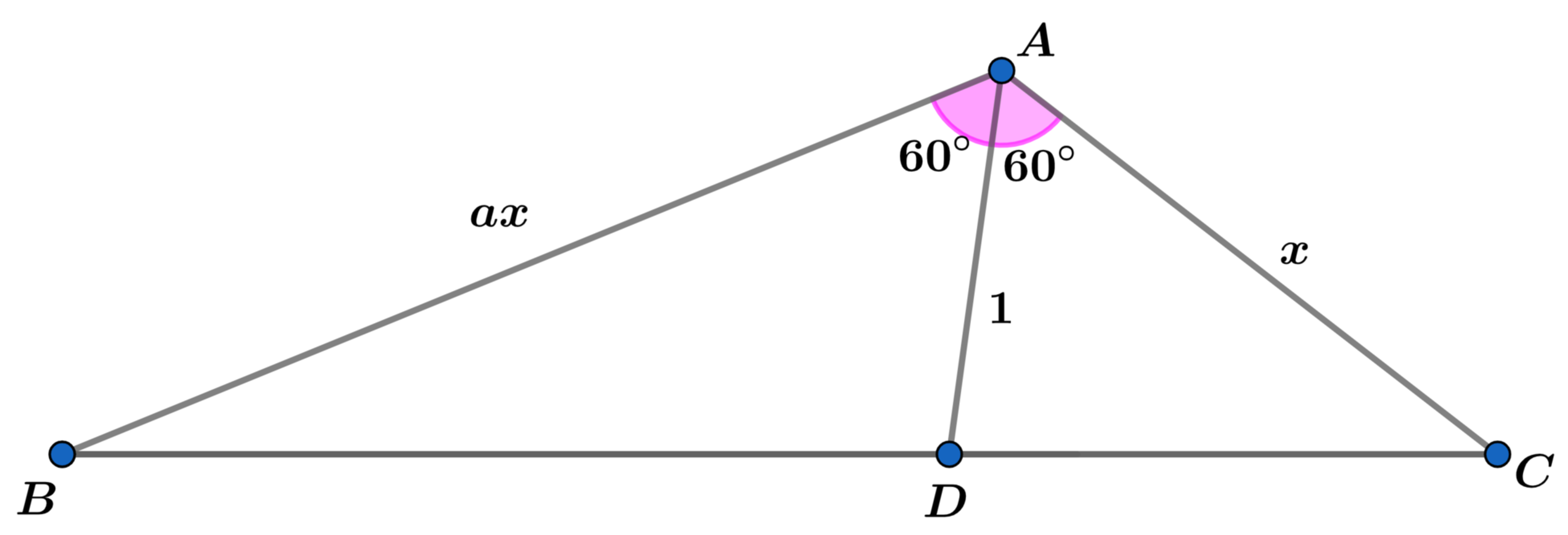
In △ A B C , A B = a x , A C = x , A D = 1 , B C = a ( a + 1 ) 2 ( a + 1 ) , m ∠ B A D = m ∠ D A C = 6 0 ∘ , and the area of △ A B C , A △ A B C = q k ϕ 3 , where ϕ = 2 1 + 5 denotes the golden ratio , and k and q are coprime positive integers. Find k + q .
The answer is 7.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
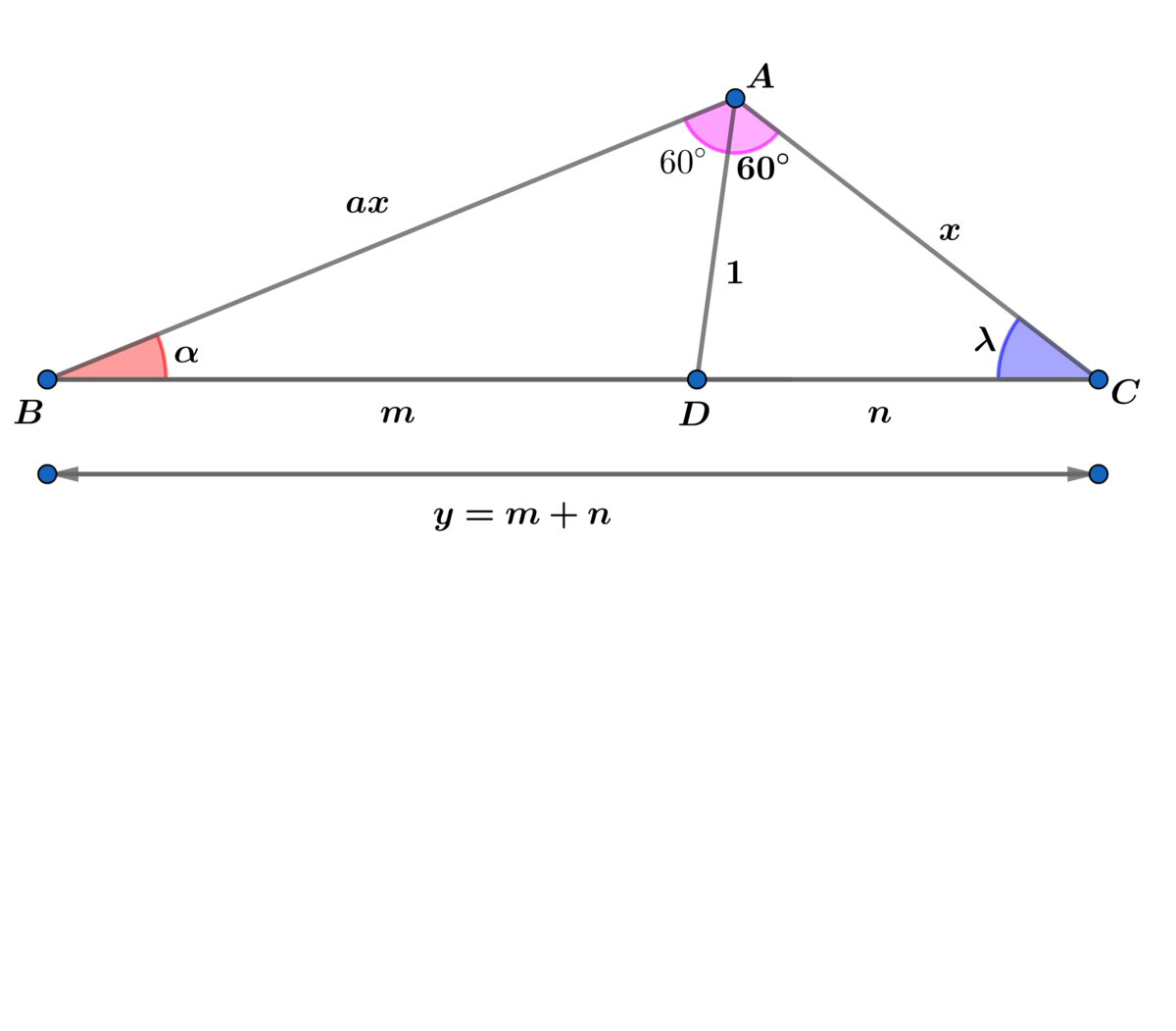
α + λ = 6 0 ∘ ⟹ α = 6 0 ∘ − λ
Using the law of cosines on △ A B C with included ∠ B A C ⟹ y = a 2 + a + 1 x = p x , where p = a 2 + a + 1 .
Using the law of sines on △ A B C ⟹ sin ( λ ) a x = sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ ) p x = 3 2 p x ⟹
sin ( λ ) = 2 p 3 a
Using the law of sines on △ D A C ⟹ sin ( λ ) 1 = sin ( 6 0 ∘ ) n = 3 2 n ⟹
n = 2 sin ( λ ) 3 = a p
Similarly using the law of sines on △ B A D ⟹ m = 2 sin ( α ) 3 = 2 sin ( 6 0 ∘ − λ ) 3 =
3 cos ( λ ) − sin ( λ ) 3 = 4 p 2 − 3 a 2 − a 2 p = 2 2 p = p
where cos ( λ ) = 2 p 4 p 2 − 3 a 2 = 2 p a + 2
⟹ y = m + n = a p ( a + 1 ) = a a + 1 a 2 + a + 1 = a a + 1 2 ( a + 1 )
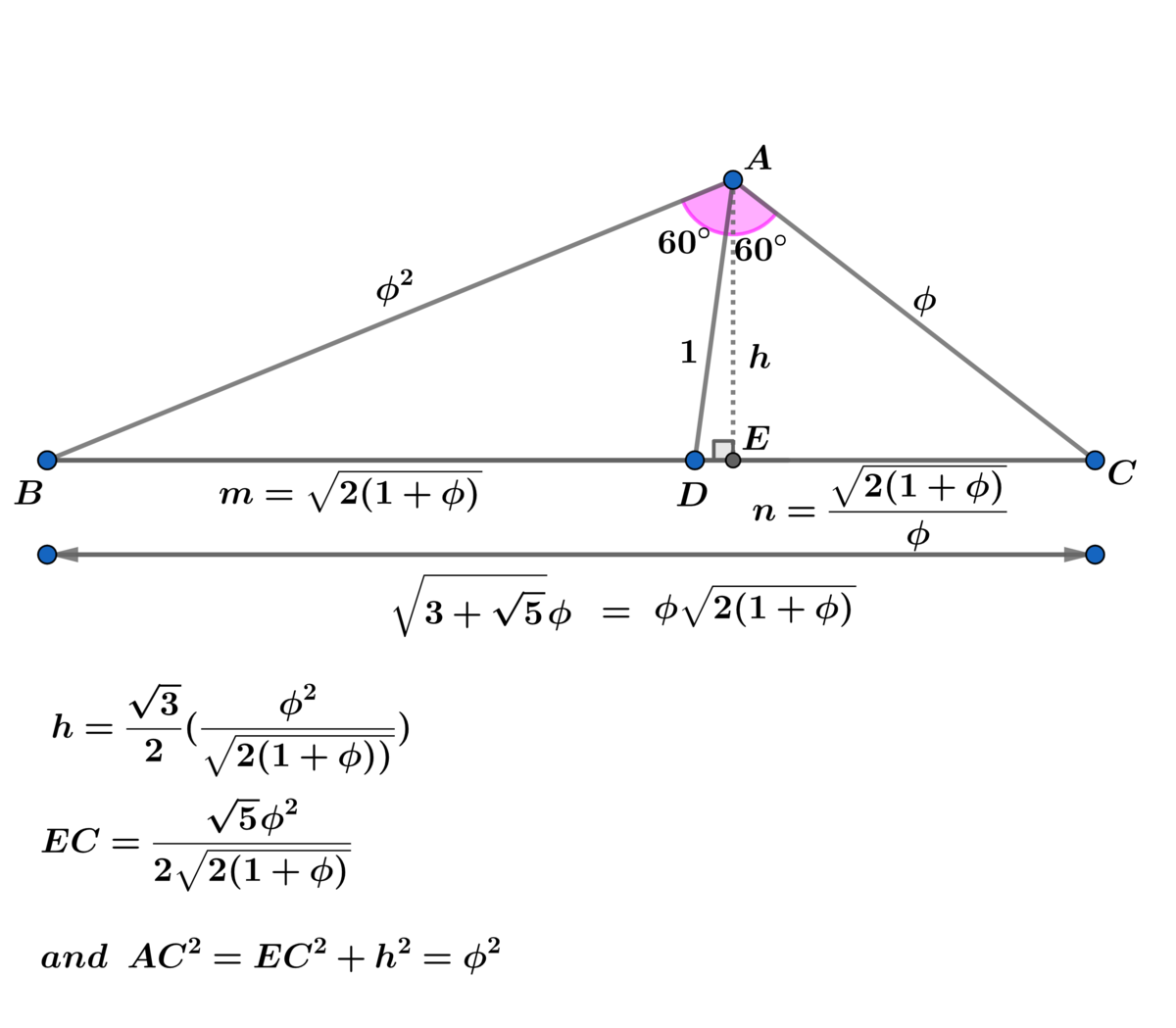
⟹ a 2 − a − 1 = 0 ⟹ a = 2 1 + 5 = ϕ , for a > 0
⟹ y = a a + 1 a 2 + a + 1 = 1 + 5 3 + 5 3 + 5 =
( 2 1 + 5 ) 3 + 5 = 3 + 5 ϕ
and y = p x = p a a + 1 ⟹ x = a a + 1 = ϕ = a
and sin ( λ ) = 2 3 p a = 2 3 3 + 5 1 ϕ
⟹ the height h = x sin ( λ ) = 2 3 3 + 5 1 ϕ 2
⟹ A △ A B C = 2 1 y h = 4 3 ϕ 3 = q k ϕ 3 ⟹ k + q = 7 .
Below is the triangle with the assigned values:
By cosine rule , { B D 2 = a 2 x 2 + 1 − 2 a x cos 6 0 ∘ = a 2 x 2 − a x + 1 D C 2 = x 2 + 1 − 2 x cos 6 0 ∘ = x 2 − x + 1
By angle bisector theorem , A B B D = C A D C ⟹ a x B D = x D C ⟹ B D = a ⋅ D C . Therefore,
B D 2 a 2 x 2 − a x + 1 a 2 x − a x ⟹ x = a 2 ⋅ D C 2 = a 2 x 2 − a 2 x + a 2 = a 2 − 1 = a ( a − 1 ) a 2 − 1 = a a + 1
By cosine rule again,
B C 2 ( a ( a + 1 ) 2 ( a + 1 ) ) 2 a 2 2 ( a + 1 ) 3 a 2 2 ( a + 1 ) 3 2 ( a + 1 ) a 2 − a − 1 ⟹ a = A B 2 + C A 2 − 2 A B ⋅ C A cos ∠ B A C = a 2 x 2 + x 2 − 2 a x 2 cos 1 2 0 ∘ = a 2 x 2 + x 2 + a x 2 = ( a 2 + a + 1 ) x 2 = ( a 2 + a + 1 ) ( a a + 1 ) 2 = a 2 + a + 1 = 0 = φ where φ is golden ratio.
Then x = φ φ + 1 = φ φ 2 = φ and A △ A B C = 2 a x ⋅ x sin 1 2 0 ∘ = 4 3 φ 3 . Therefore k + q = 3 + 4 = 7 .