It's All Logs
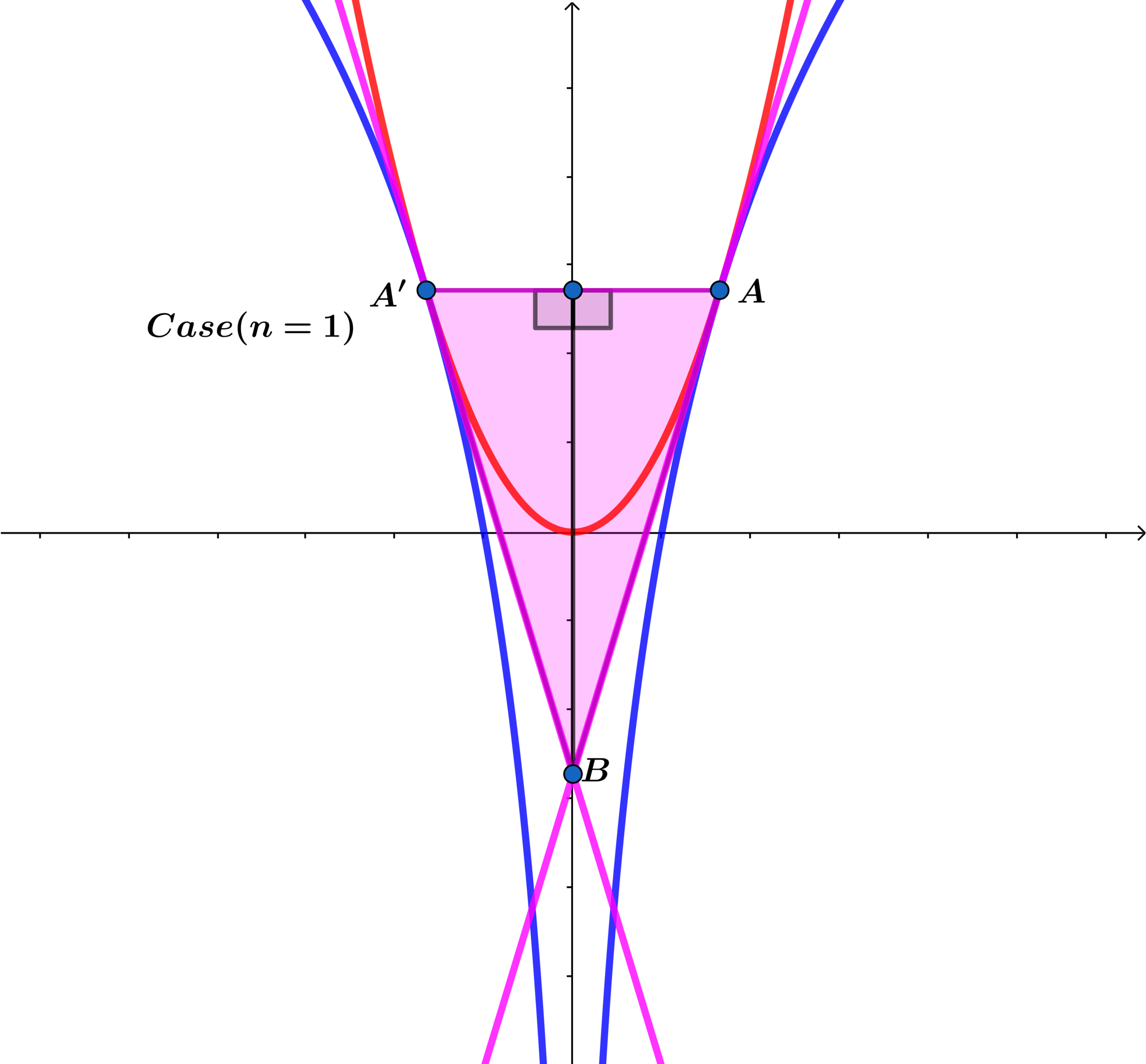
Let be a positive integer and and .
and have common tangents at points and and the tangent lines intersect at forming as shown above.
If is the area under the curve on the interval , find the value of for which .
The answer is 3.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Using the symmetry about the y axis we have:
f ( x ) = x 2 n and g ( x ) = lo g b ( x ) = ln ( b ) ln ( x ) ⟹ f ′ ( a ) = 2 n a 2 n − 1 = g ′ ( a ) = a ln ( b ) 1 ⟹ a 2 n = 2 n ln ( b ) 1 ⟹ a = ( 2 n ln ( b ) 1 ) 2 n 1
and
a 2 n = ln ( b ) ln ( a ) ⟹ 2 n ln ( b ) 1 = 2 n ln ( b ) ln ( 2 n ln ( b ) 1 )
⟹ 1 = ln ( 2 n ln ( b ) 1 ) ⟹ 2 n ln ( b ) = e 1 ⟹ ln ( b ) = 2 n e 1 ⟹ b = e 2 n e 1 ⟹ a = e 2 n 1 and a 2 n = e .
Using A ( e 2 n 1 , e ) ⟹ y − e = 2 n e 2 n 2 n − 1 ( x − e 2 n 1 )
and using symmetry about the y axis we have A ′ ( − e 2 n 1 , e ) ⟹ y − e = − 2 n e 2 n 2 n − 1 ( x + e 2 n 1 )
Solving the two equations above we obtain B ( 0 , ( 1 − 2 n ) e )
Using points A , A ′ , B and C ( 0 , e ) we have A A ′ = 2 e 2 n 1 and B C = 2 n e ⟹ A △ A A ′ B = 2 n e 2 n 2 n + 1
and
A p = ∫ − e 2 n 1 e 2 n 1 x 2 n = 2 n + 1 2 e 2 n 2 n + 1
⟹ A p A △ A A ′ B = n ( 2 n + 1 ) = 2 n 2 + n = n + 1 8 ⟹ 2 ( n − 3 ) ( n + 3 ) = 0 and n = − 3 ⟹ n = 3 .