It's all Symmetry.
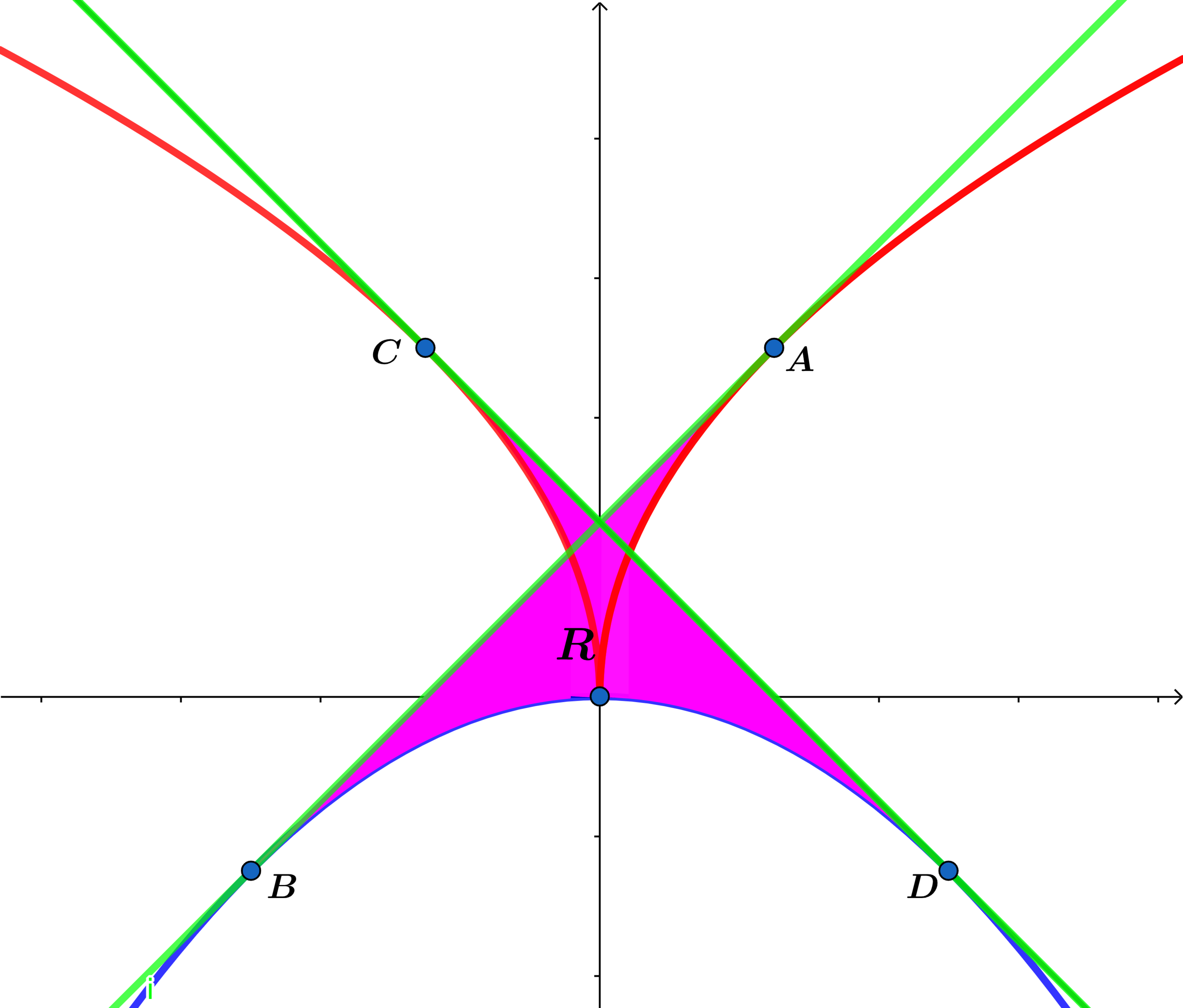
Let and .
If and have common tangents at points and and and respectively, find the area of the region above to eight decimal places.
The answer is 0.09640452.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let f ( x ) = ∣ x ∣ and g ( x ) = − x 2 and A : ( x 0 , y 0 ) .
R ( 0 , 0 ) ∘ R y = x ( x 0 , y 0 ) = ( − y 0 , − x 0 ) = B
and R y − a x i s ( − y 0 , − x 0 ) = ( y 0 , − x 0 ) = D and R y − a x i s ( x 0 , y 0 ) = ( − x 0 , y 0 ) = C
⟹ m A B = 1 and m C D = − 1
m A B = 1 ⟹ f ′ ( x 0 ) = 2 x 0 1 = 1 ⟹ x 0 = 4 1 ⟹ y 0 = 2 1 ⟹ y = x + 4 1
and m C D = − 1 ⟹ y = − x + 4 1
To find the x coordinate of the find point of intersection E of y = − x + 4 1 and f ( x ) = x
let − x + 4 1 = x ⟹ 1 − 4 x = 4 x ⟹ 1 − 8 x + 1 6 x 2 = 1 6 x ⟹ 1 6 x 2 − 2 4 x + 1 = 0 ⟹ x = 4 3 ± 2 2
We drop x = 4 3 + 2 2 which doesn't satisfy the initial equation and choose x = 4 3 − 2 2 which satisfies the initial equation.
For A R 1 we have:
A R 1 = ∫ 0 4 1 x + 4 1 − x 2 1 d x = 2 1 x 2 + 4 1 x − 3 2 x 2 3 ∣ 0 4 1 = 9 6 1
For A R 2 we have:
A R 2 = ∫ 0 4 3 − 2 2 x 2 1 + x 2 d x = 3 2 x 2 3 + 3 1 x 3 ∣ 0 4 3 − 2 2 =
3 2 ( 4 3 − 2 2 ) 2 3 + 3 1 ( 4 3 − 2 2 ) 3 .
For A R 3 we have:
A R 3 = ∫ 4 3 − 2 2 2 1 ( − x + 4 1 + x 2 ) d x =
− 2 1 x 2 + 4 1 x + 3 1 x 3 ∣ 4 3 − 2 2 2 1 =
2 4 1 − ( − 2 1 ( 4 3 − 2 2 ) 2 + 4 1 ( 4 3 − 2 2 ) + 3 1 ( 4 3 − 2 2 ) 3 )
A R 2 + A R 3 = ( 4 3 − 2 2 ) ( 2 4 8 3 − 2 2 + 3 − 6 2 ) + 2 4 1
The Area A ∗ = A R 1 + A R 2 + A R 3 = 9 6 1 [ 5 + ( 3 − 2 2 ) ( 8 3 − 2 2 + 3 − 6 2 ) ]
Using the symmetry about the y axis the total area A = 2 A ∗ =
9 6 2 [ 5 + ( 3 − 2 2 ) ( 8 3 − 2 2 + 3 − 6 2 ) ] ≈ 0 . 0 9 6 4 0 4 5 2