It's All Triples 2
Let be a positive even integer.
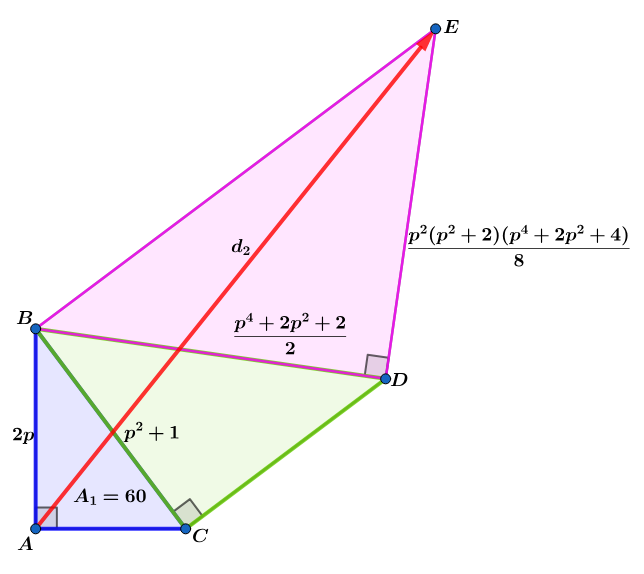
Given area , find the distance above.
The answer is 10517.65850528.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
This problem was created using a general recursive sequence that I derived using primitive pythagorean triples.
Below is the recursive sequence.
Let
a 1 = m 1 2 + n 1 2
b 1 = 2 m 1 n 1
c 1 = m 1 2 + n 1 2 ,
where ( m 1 , n 1 ) = 1 , m 1 > n 1 and m 1 is even and n 1 is odd.
for ( 1 ≤ j ≤ n − 1 ) let
a j + 1 = c j
b j + 1 = 2 ( c j + 1 ) ( c j − 1 )
c j + 1 = 2 c j 2 + 1
then for each ( 1 ≤ k ≤ n ) ( a k , b k , c k ) is a primitive pythagorean triple.
Let p be a positive even integer with m 1 = p and n 1 = 1 .
Using the above the first ppt triple is ( p 2 − 1 , 2 p , p 2 + 1 ) ⟹ A 1 = 2 1 ( 2 p ) ( p 2 − 1 ) = 6 0 ⟹ p 3 − p − 6 0 = 0 ⟹ ( p − 4 ) ( p 2 + 4 p + 1 5 ) = 0 ⟹ p = 4
⟹ ( p 2 − 1 , 2 p , p 2 + 1 ) = ( 1 5 , 8 , 1 7 ) .
The second ppt triple is ( p 2 + 1 , 2 ( p 2 + 2 ) ∗ p 2 , 2 p 4 + 2 p 2 + 2 ) = ( 1 7 , 1 4 4 , 1 4 5 )
The third ppt triple is ( 2 p 4 + 2 p 2 + 2 , 8 p 2 ( p 2 + 2 ) ( p 4 + 2 p 2 + 4 ) , 8 p 8 + 4 p 6 + 8 p 4 + 8 p 2 + 8 ) = ( 1 4 5 , 1 0 5 1 2 , 1 0 5 1 3 ) .
cos ( θ 1 ) = 1 7 8 , sin ( θ 1 ) = 1 7 1 5
cos ( θ 2 ) = 1 4 5 1 7 , sin ( θ 2 ) = 1 4 5 1 4 4
cos ( θ 3 ) = 1 0 5 1 3 1 4 5 , sin ( θ 3 ) = 1 0 5 1 3 1 0 5 1 2
⟹ cos ( θ 1 + θ 2 + θ 3 ) =
cos ( θ 1 ) cos ( θ 2 ) cos ( θ 3 ) − sin ( θ 1 ) sin ( θ 2 ) cos ( θ 3 ) − sin ( θ 1 ) sin ( θ 3 ) cos ( θ 2 ) − sin ( θ 2 ) sin ( θ 3 ) cos ( θ 1 ) =
1 0 5 1 3 8 − ( 1 7 ) ( 1 0 5 1 3 ) ( 1 5 ) ( 1 4 4 ) − ( 1 0 5 1 3 ) ( 1 4 5 ) ( 1 5 ) ( 1 0 5 1 2 ) − ( 1 4 5 ) ( 1 0 5 1 3 ) ( 1 7 ) ( 1 4 4 ) ( 1 0 5 1 2 ) ( 8 ) = − 2 5 9 1 4 5 4 5 1 5 0 8 3 8 6 4
⟹
d 2 = A E = 8 2 + 1 0 5 1 3 2 + 2 5 9 1 4 5 4 5 ( 2 ) ( 8 ) ( 1 0 5 1 3 ) ( 1 5 0 8 3 8 6 4 ) = 2 4 6 5 2 7 2 6 8 1 1 1 1 1 6 9 ≈ 1 0 5 1 7 . 6 5 8 5 0 5 2 8 .
Note: For the general recursive sequence above the sum of the squares a 1 2 + ∑ j = 1 n b j 2 = c n 2 .
For this problem with p = 4 we have: 1 5 2 + 8 2 + 1 4 4 2 + 1 0 5 1 2 2 = 1 0 5 1 3 2 .
Also note given ( a 1 , b 1 , c 1 ) and setting m j + 1 − n j + 1 = 1 and m j + 1 + n j + 1 = c j ⟹ m j + 1 = 2 c j + 1 and n j + 1 = 2 c j − 1 and replacing m j + 1 , n j + 1 into a j + 1 = ( m j + 1 − n j + 1 ) ( m j + 1 + n j + 1 ) , b j + 1 = 2 m j + 1 n j + 1 , c j + 1 = ( m j + 1 ) 2 + ( n j + 1 ) 2
⟹
a j + 1 = c j
b j + 1 = 2 ( c j + 1 ) ( c j − 1 )
c j + 1 = 2 c j 2 + 1
and for each j such that ( 1 ≤ j ≤ n ) c j is odd ⟹ a j , b j and c j are positive integers and ( c j , 2 c j 2 − 1 , 2 c j 2 − 1 + 1 ) = 1 and a j 2 + b j 2 = c j 2 .