JEE-Advanced 2015 (1/40)
4 5 cos 2 2 x + cos 4 x + sin 4 x + cos 6 x + sin 6 x = 2
If x is a real number that satisfy the equation above, find the number of distinct solution(s) of x in the interval [ 0 , 2 π ] .
The answer is 8.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
Moderator note:
Can you solve this without graphing?
cos ( 4 x ) = 0 2 cos 2 ( 2 x ) − 1 cos 2 ( 2 x ) = 2 1 ( 2 cos 2 x − 1 ) 2 = 2 1 cos 4 x − cos 2 x = − 8 1 Let cos 2 x = x . Then: x 2 − x + 8 1 = 0 x = 2 1 − 2 2 1 and x = 2 1 + 2 2 1 First case, cos 2 x = 2 1 − 2 2 1 cos x = 2 1 − 2 2 1 So x = 2 n π ± cos − 1 ( ± 2 1 − 2 2 1 ) So in all, 4 solutions and similarly for the second case 4 solutions.
Cos 4x=0 x=(2n-1)(pi/2) Put n=1 to 8 so 8 solutions
Substitute \cos{4x}=1- 2\sin^2 {2x} and you will get
\sin^2 {2x} =\frac{1}{10}
Where 2x is in interval [0 , 4\pi] which we know will happen 8 times. Simple
Perfect Solution! . used exactly the same approach
4 5 cos 2 2 x + cos 4 x + sin 4 x + cos 6 x + sin 6 x = 4 5 cos 2 2 x + 1 − 2 sin 2 x cos 2 x + cos 4 x + sin 4 x − sin 2 x cos 2 x = 4 5 cos 2 2 x + 1 − 2 1 sin 2 2 x + 1 − 2 sin 2 x cos 2 x − 4 1 sin 2 2 x = 2 + 4 5 cos 2 2 x − 2 1 sin 2 2 x − 2 1 sin 2 2 x − 4 1 sin 2 2 x = 2 + 4 5 cos 2 2 x − 4 5 sin 2 2 x = 2 + 4 5 cos 4 x = 2 ⇒ cos 4 x = 0
For the domain [ 0 , 2 π ] , the function y = cos 4 x cuts the x axis at 8 points.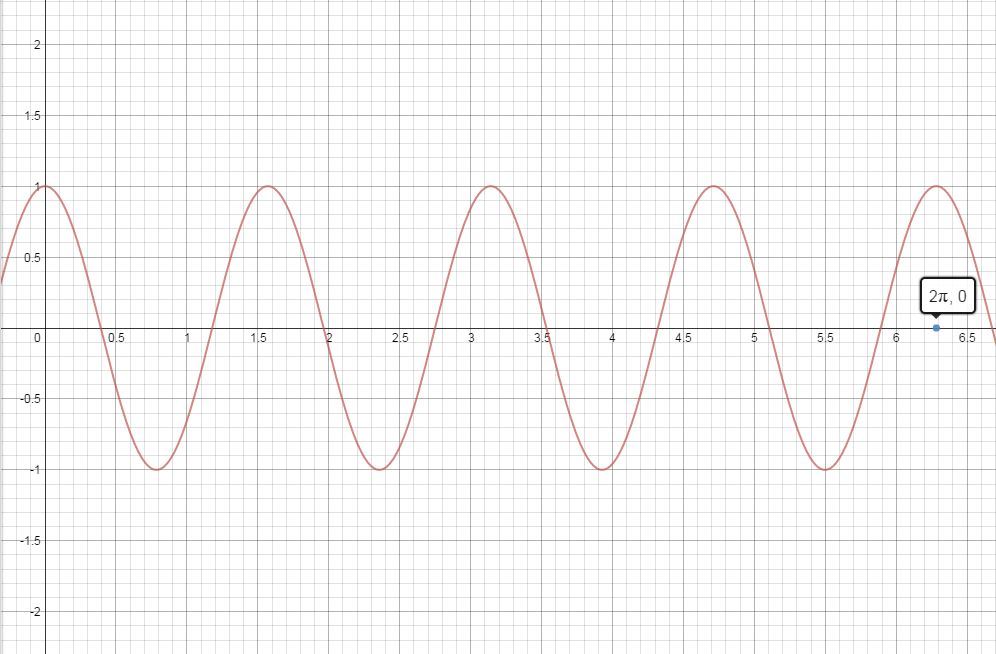
Hence the number of distinct solutions = 8