Joining
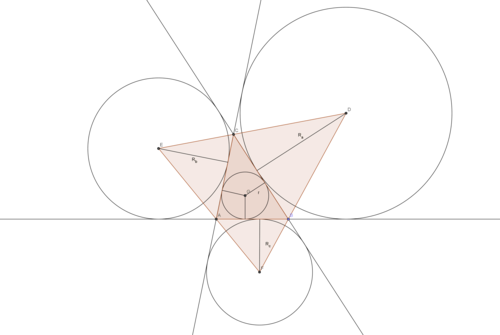 In triangle
△
A
B
C
, let
B
C
=
7
,
A
C
=
6
and
A
B
=
5
. Let
D
,
E
and
F
be the centers of the excircles relatives to
B
C
,
A
C
and
A
B
respectively.
In triangle
△
A
B
C
, let
B
C
=
7
,
A
C
=
6
and
A
B
=
5
. Let
D
,
E
and
F
be the centers of the excircles relatives to
B
C
,
A
C
and
A
B
respectively.
If E F = g c a , D F = g d a b and D E = f b , where a b is square free, g cd ( c , g ) = 1 and g cd ( d , g ) = 1 , find a b c − d f g .
The answer is 460.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Good solution. Is my solution good enough
An important trick is to use here half-angle fomuales.
First note that E F = E A + F A , D F = D B + F B , D E = D C + E C
We drop the perpendiculars from D , E , F on B C , A C , A B respectively and name them G , H , I respectively.
It is easy to see that ∠ H E A = 2 A a n d ∠ I F A = 2 A and similarly for others.
So we have E F = E G s e c ( 2 A ) + F I s e c ( 2 A ) = ( r 2 + r 3 ) s e c ( 2 A ) (i)
We will use r 1 = s ( t a n 2 A ) , r 2 = s ( t a n 2 B ) , r 3 = s ( t a n 2 C ) in (i) to get :
EF= s ( s e c ( 2 A ) ) ( ( t a n 2 B ) + ( t a n 2 C ) )
We will use t a n 2 B = Δ ( s − a ) ( s − b ) , t a n 2 C = Δ ( s − a ) ( s − b ) to get
E F = ( s e c 2 A ) Δ a s ( s − a ) = a s e c 2 A c o t 2 A = s i n 2 A a ( U s i n g t a n 2 A = s ( s − a ) Δ )
Similarly D F = s i n 2 B b , D E = s i n 2 C c
Finally use s i n 2 A = b c ( s − b ) ( s − c ) , s i n 2 B = a c ( s − a ) ( s − c ) , s i n 2 C = a b ( s − a ) ( s − b ) to get the values.
Nice solution :D
First we find the area of △ A B C using Heron's formula, and it's: [ A B C ] = 6 6 . Now, we find the length of the three excircles with the known formulas:
R a = − B C + A B + A C 2 [ A B C ] = 4 1 2 6 = 3 6 R b = B C + A B − A C 2 [ A B C ] = 6 1 2 6 = 2 6 R c = B C − A B + A C 2 [ A B C ] = 8 1 2 6 = 2 3 6
With the lengths of the exradius, we find the area of △ B D C , △ C E A and △ A B F , because the exradius are the altitudes and each side is the base:
[ B D C ] = 2 B C × R a = 2 7 × 3 6 = 2 2 1 6 [ C E A ] = 2 A C × R b = 2 6 × 2 6 = 6 6 [ A B F ] = 2 A B × R c = 2 5 × 2 3 6 = 4 1 5 6
Clearly, if we sum the four areas we obtained, we obtain the area of △ D E F :
[ D E F ] = [ A B C ] + [ B D C ] + [ C E A ] + [ A B F ] [ D E F ] = 6 6 + 2 2 1 6 + 6 6 + 4 1 5 6 = 4 1 0 5 6
Next, with a little angle chasing, we find out that:
∠ D = 2 ∠ B + ∠ C , ∠ E = 2 ∠ A + ∠ C and ∠ F = 2 ∠ A + ∠ B
Our goal now is to find the sines of every angle, to do that we first obtain the sines of △ A B C using law of cosines, then apply the angle sum and finally the formula for a half angle. We obtain:
sin ∠ D = 5 1 5 , sin ∠ E = 3 5 3 1 0 5 and sin ∠ F = 7 4 2
At this point we have the area of △ D E F and every of its three angles. With law of sines and its formulas for the area of triangle, we will find every side:
[ D E F ] = 2 D E × D F × sin ∠ D
[ D E F ] = 2 D E × E F × sin ∠ E
[ D E F ] = 2 D F × E F × sin ∠ F
Substitute with the known values and simplify:
4 1 0 5 6 = 1 0 D E × D F × 1 5 ⇒ D E × D F = 2 1 0 5 1 0
4 1 0 5 6 = 7 0 D E × E F × 3 1 0 5 ⇒ D E × E F = 2 3 5 7 0
4 1 0 5 6 = 1 4 D F × E F × 4 2 ⇒ D F × E F = 2 1 0 5 7
To solve that system, multiply the three equations, simplify and let the three sides to be in the left hand side:
( D E × D F × E F ) 2 = 4 1 3 5 0 5 6 2 5
Take square root to both sides:
D E × D F × E F = 2 3 6 7 5
Finally, divide every of the three equations with this one to obtain every side:
E F = 2 1 0 5 1 0 2 3 6 7 5 = 2 7 1 0
D F = 2 3 5 7 0 2 3 6 7 5 = 2 3 7 0
D E = 2 1 0 5 7 2 3 6 7 5 = 5 7
Hence, a = 1 0 , b = 7 , c = 7 , d = 3 , f = 5 , g = 2 and a b c − d f g = 4 6 0 .
Note: if you try to generalize it for sides B C = a , A C = b and A B = c , you would obtain this interesting simple formulas:
d = E F = ( a + b − c ) ( a − b + c ) 2 a b c e = D F = ( − a + b + c ) ( a + b − c ) 2 b a c f = D E = ( − a + b + c ) ( a − b + c ) 2 c a b