Just an Angle!
Find P C .
Note: This length can be expressed as B A , where A , B are coprime positive integers. Submit the value of A + B as your answer.
The answer is 79.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
9 solutions
Thinking outside the box. Short and sweet. Excellent approach.
Let P C = x and ∠ A P C = θ , then using sine rule, we have:
sin 9 0 ∘ x = x ⇒ 2 ( sin ( 6 0 ∘ − θ ) ) 2 ( 2 3 cos θ − 2 1 sin θ ) 3 cos θ − sin θ 3 cos θ 3 cos 2 θ 3 ( 1 − sin 2 θ ) 3 ⇒ sin θ ⇒ x ⇒ A + B = sin θ 2 = sin ( 6 0 ∘ − θ ) 3 = 3 sin θ = 3 sin θ = 3 sin θ = 4 sin θ = 1 6 sin 2 θ = 1 6 sin 2 θ = 1 9 sin 2 θ = 1 9 3 = sin θ 2 = 1 9 3 2 = 3 7 6 = 7 6 + 3 = 7 9
verı got...
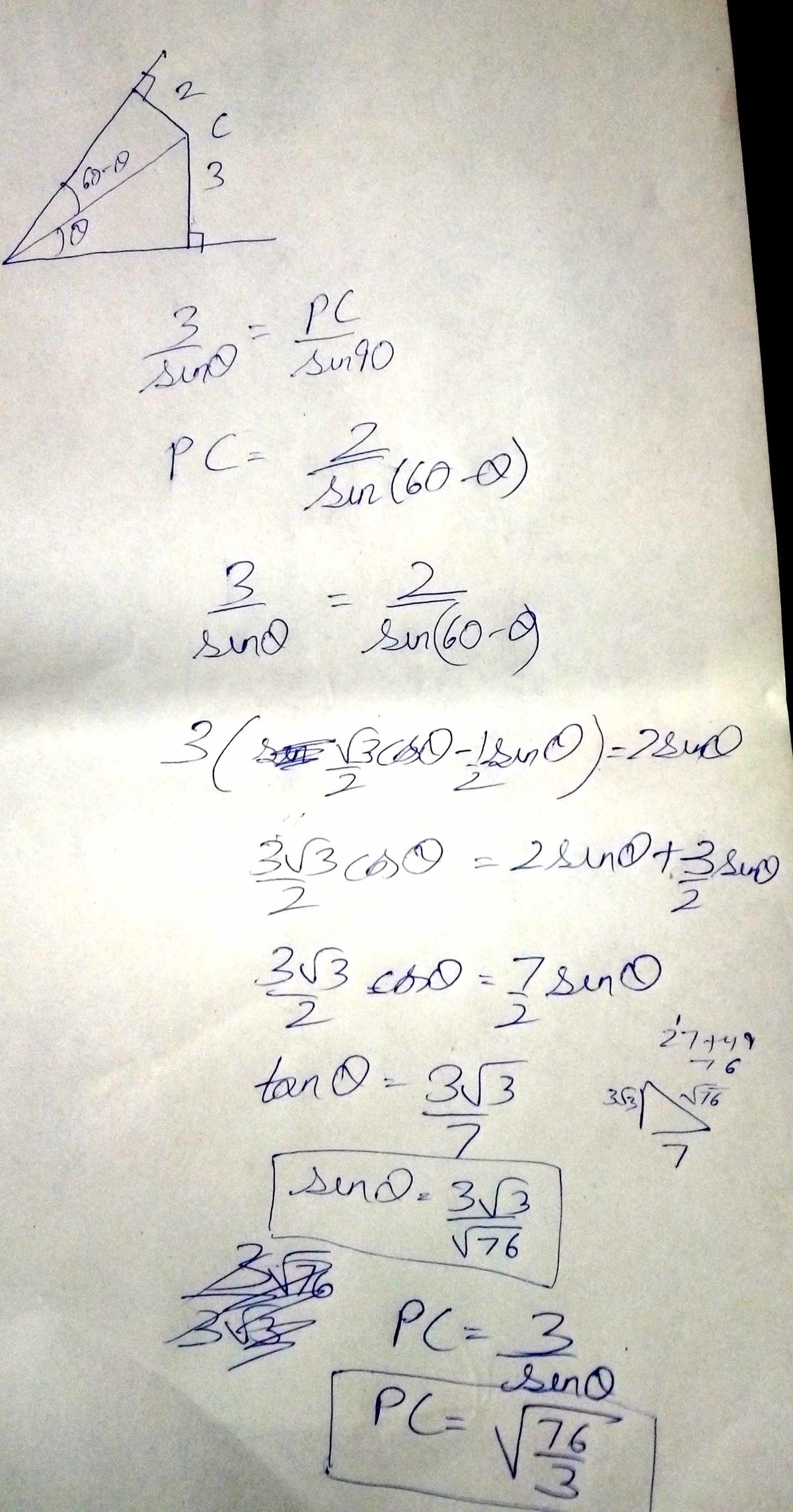
I used sine rule in the very first step
Brilliant! This is a usual solution. Can you think of other solutions? Shorter ones?
Extend the line BC to intersect extension of line AP at point D.
DAC=30 degrees
CD=2/sin(60)=4
BP=7tan(30)=7/sqrt(3)
CP^2=BP^2+BC^2
CP=sqrt(76/3)
That's what I have used. It's a simple problem though.
P = ( 0 , 0 ) C = ( x , 3 ) A P : y = tan 3 π x ⟹ 3 x − y = 0 3 2 + 1 2 ∣ 3 x − 3 ∣ = 2 ∣ 3 x − 3 ∣ = 2 ⟹ ∣ 3 x − 3 ∣ = 4 ⟹ x = 3 7 Other solution is extraneous C P = x 2 + 9 = 3 4 9 + 9 = 3 7 6 ⟹ 7 6 + 3 = 7 9
Nice use of co-ordinate geometry!
Let the radius be x then x²+x²-2x.xcos120 = 4 + 9 - 2.2.3.cos120. Then x = sqrt(19/3). PC is diameter so PC = 2x = sqrt(76/3). Sry cant use latex im confused
C can be found as intersection of 2 lines:
- Line1 parallel with AP at distance 2: y=sqrt(3).x-4
- Line2 : y=3
So the x coordinate of C is 7/sqrt(3)
-> PC=sqrt(3^2 + (7/sqrt(3))^2)=sqrt(76/3)
Here I present a proof using coordinate geometry.
Let P = ( 0 , 0 ) and B = ( b , 0 ) , where b > 0 . Then O = ( b , 3 ) . Now
S l o p e O A = S l o p e O B − 1 = t a n 6 0 ∘ − 1 = − t a n 3 0 ∘ ,
and O A = 2 with A to the left of O so the point A = ( b − 2 c o s 3 0 ∘ , 3 + 2 s i n 3 0 ∘ ) = ( b − 3 , 4 ) .
Now, the slope of P A is t a n 6 0 ∘ = 3 , so
b − 3 4 = 3 , giving b = 3 7 .
Therefore P C = b 2 + 9 = 3 4 9 + 9 = 3 7 6 , and so
A + B = 7 6 + 3 = 7 9 .
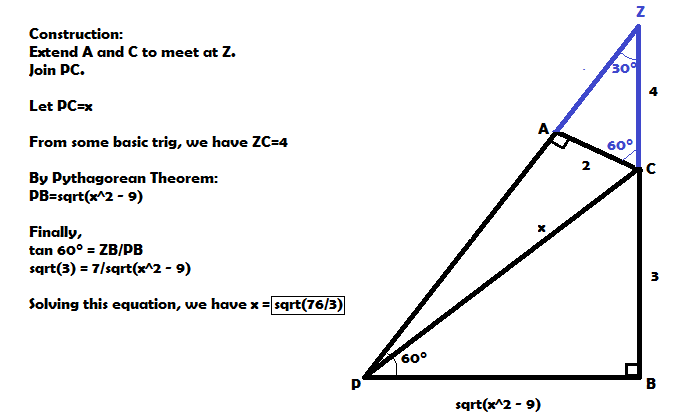
Extend P B and A C , label the point of intersection as E .
We have ∠ A E P = 3 0 ∘ , ⇒ C E = 6 , A E = 8 , ⇒ A P = 3 8 3 , ⇒ P C = 2 2 + ( 3 8 3 ) 2 = 3 2 5 7 = 9 4 × 5 7 = 3 7 6 .