Keeping The School Clean
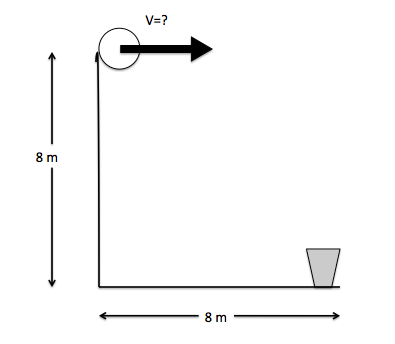
Juan plans to put a paper ball in the trash can that is at the ground level of his school's building. Juan is on the third floor, 8 . 0 0 m above the ground level and the trash can is 8 . 0 0 m away from the building where Juan is. If Juan wants to throw the paper ball horizontally, with what velocity should he throw it?
Give your answer in meters per second and take the value of acceleration due to gravity as 9 . 8 0 m/s 2 .
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Based on a national competition.
The answer is 6.26.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Well just check if my solution is right... The rate of falling of the paper ball will not be affected by horizontal motion. Therefore the time taken for the paper ball to fall into the trash 8m below is 0.8163s. Hence the paper ball has to travel 8m in the horizontal direction in 0.8163s. That'll be 8m In 0.8163s.
Log in to reply
You've got the idea but you obtained the time by dividing the height by the acceleration... We can model the vertical position of the paper ball as: y = h − 2 g t 2 so, to get to the ground (y=0) it would take it a time: t = g 2 h
According to the solution given the trash can is vertically below the place from where it is thrown which is contradictory to the question. Can u give a more convincing reply?
Log in to reply
May the question is not very clear. I edited it; I think it should be easier to understand. Give it a look, what do you think?
I took this route; (assumed there's no air friction, than we would've needed the area of the ball) Maximum kinetic energie should be equal to the maximum potential energie; So 0.5m * v^2 = m * g * h Therefore 0.5 v^2 = gh Thus v=sqrt(2gh) While this seems correct to me, how did I misplace "the divided by 2" with "times 2"?
Log in to reply
I'm sorry, but that is not the way to solve it /: You just solved for the velocity's vertical component in the moment when the paper ball gets to the trash can. The problem asks for the horizontal velocity needed for getting the ball there; this problem is more about kinematics and, although energies might be used to help you solve the problem, you can't use only energies.
It is a projectile motion. We know, s=ut+1/2gt² 8=1/2x9.8t² t=1.277s So, v=d/t V=8/1.277 v=6.26m/s
This problem can be solved using simple Kinematics. Since there is no acceleration in the "x" direction, the initial velocity should satisfy:
V = t d where "d" is the distance between the trash can and the building
The paper ball takes a time "t" to get to the ground:
t = g 2 h where "h" is the height of the third floor
In this case, d = h . So:
V = 2 g d ≈ 6 . 2 6 s m