This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Considering the periodicity of sine and cosine, we can solve this problem easily.
Below is a graph of sin ( cos ( x ) ) (in red), marked by the limits of the given integral ∫ 4 3 π π sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x with the red line being x = 4 3 π and the black line being x = π .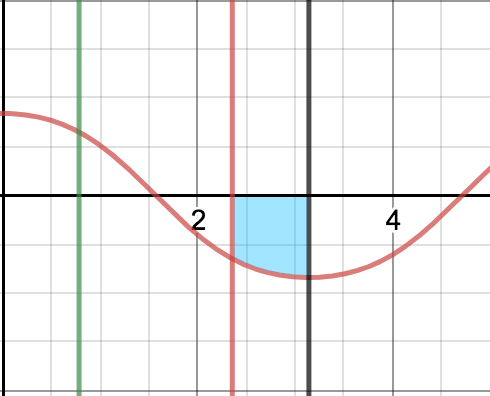
The problem states that the area in between x = 4 3 π and x = π is 0.613, indicated by the blue shaded region above. As sine and cosine are both periodic with period 2 π , the periodic function sin ( cos ( x ) ) must also be periodic with a period of 2 π . With the knowledge that sin ( cos ( x ) ) is periodic with the period 2 π , we can establish the identity that,
sin ( cos ( x ± 2 π ) ) = sin ( cos ( x ) )
Next, as sin ( cos ( x ) ) is an odd function, we can say that
sin ( cos ( − x ± 2 π ) ) = − sin ( cos ( x ) )
With the aforementioned identity, we can conclude that for any point x within the set of [ 4 3 π , π ], the value given by the sin(cos) of the corrospoding point x ± 2 π will be equal to that of the originial point, by identity one. Meaning,
∫ 4 3 π π sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x = ∫ 0 4 π sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x = ∫ 4 3 π π sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x = 0 . 6 1 3
extended to other points,
∫ − 2 π 2 − 3 π sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x = ∫ 2 − π 0 sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x = 2 1 ∫ 2 − 3 π 2 − π sin ( cos ( x ) ) d x = A
Graphically,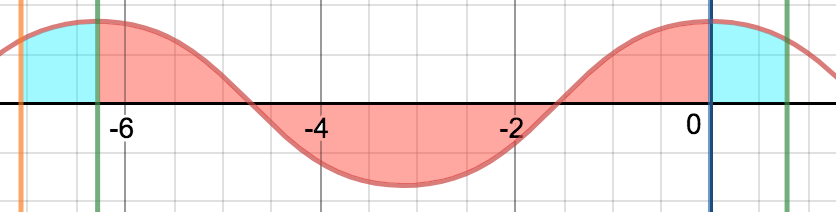 So,
So,
I = A − 2 ∗ ( 2 1 A ) + 2 ( 0 . 6 1 3 ) = 1 . 2 6 6 as illustrated by the graph above.