Let's boycott Calculus this time! (Part 3)
Find the maximum value of sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 5 cos 2 x 1 correct to 3 decimal places.
If you think that no maximum value exists but a minimum value does, then enter the minimum value. If you think that no global extrema exist for this function, then enter your answer as 666.
The answer is 2.000.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Let's handle the denominator of the function first:
= sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 5 cos 2 x
= 1 − cos 2 x + 1 . 5 ( 2 sin x cos x ) + 5 cos 2 x
= 1 . 5 sin 2 x + 4 cos 2 x + 1
= 1 . 5 sin 2 x + 4 cos 2 x − 2 + 3
= 1 . 5 sin 2 x + 2 ( 2 cos 2 x − 1 ) + 3
= 1 . 5 sin 2 x + 2 cos 2 x + 3
Clearly the function will have a maximum value when its denominator will be minimum and positive .
We know that for constants a and b , − a 2 + b 2 ⩽ a sin x + b cos x ⩽ a 2 + b 2 is true. (Proof at the ending).
Hence, for our case, − 1 . 5 2 + 2 2 ⩽ 1 . 5 sin x + 2 cos x ⩽ 1 . 5 2 + 2 2
⟹ − 6 . 2 5 + 3 ⩽ 1 . 5 sin x + 2 cos x + 3 ⩽ 6 . 2 5 + 3 . ⟹ 0 . 5 ⩽ 1 . 5 sin x + 2 cos x + 3 ⩽ 5 . 5 . ⟹ 0 . 5 ⩽ sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 5 cos 2 x ⩽ 5 . 5 .
Hence, it's minimum value is positive. Therefore the function sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 5 cos 2 x 1 will attain its maximum value when sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 5 cos 2 x = 0 . 5 . Hence substituting, the maximum value is 2 .
PROOF for − a 2 + b 2 ⩽ a sin x + b cos x ⩽ a 2 + b 2 :
Consider a right angled triangle with height a and base b and trigonometric angle y . Then a 2 + b 2 a = sin y and a 2 + b 2 b = cos y .
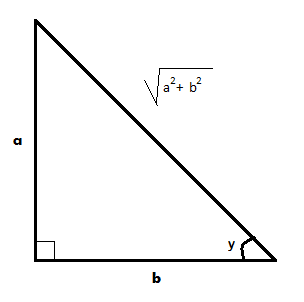
Now, a sin x + b cos x = a 2 + b 2 [ a 2 + b 2 a sin x + a 2 + b 2 b cos x ] = a 2 + b 2 [ sin y sin x + cos y cos x ] = a 2 + b 2 cos ( x − y ) .
We know that − 1 ⩽ cos ( x − y ) ⩽ 1 ⟹ − a 2 + b 2 ⩽ a 2 + b 2 cos ( x − y ) ⩽ a 2 + b 2 [Since a 2 + b 2 is always positive]
⟹ − a 2 + b 2 ⩽ a sin x + b cos x ⩽ a 2 + b 2
Question Source: IIT JEE Paper 2010 - Problem 48.
Nice approach :) (+1)
I did using calculus. The denominator is simply 1 + 4 c o s 2 x + 3 s i n ( 2 x ) / 2 . So we want denominator to be minimum.Just differentiate the denominator to get T a n 2 x = 3 / 4 Now it's minimum when s i n ( 2 x ) a n d c o s ( 2 x ) are both negative. Proceed to get the final answer as 2.

y = sin 2 x + 3 sin x cos x + 5 cos 2 x 1 = 1 + 3 sin x cos x + 4 cos 2 x 1 = 1 + 2 3 ( 2 sin x cos x ) + 2 ( 2 cos 2 x − 1 ) + 2 1 = 2 3 sin 2 x + 2 cos 2 x + 3 1 = 2 5 ( 5 3 sin 2 x + 5 4 cos 2 x ) + 3 1 = 2 5 sin ( 2 x + tan − 1 3 4 ) + 3 1 As sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1
We note that y is maximum when the denominator 2 5 sin ( 2 x + tan − 1 3 4 ) + 3 is minimum. The denominator is minimum when sin ( 2 x + tan − 1 3 4 ) = − 1 , the minimum.
⟹ y m a x = 2 5 ( − 1 ) + 3 1 = 2