Limits and Integral of transcendental function
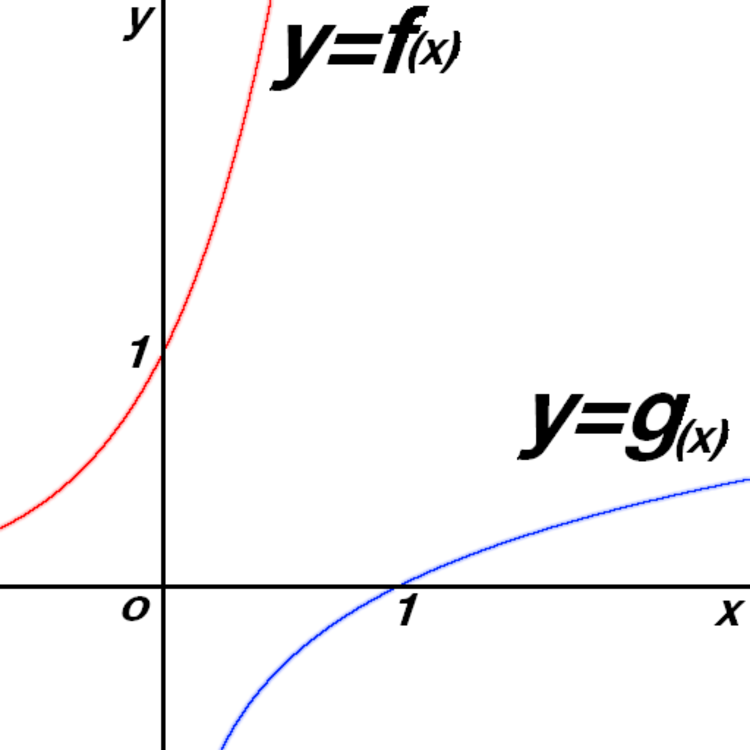 This is graph of function
and its inverse function
(where
e
is base of natural logarithm)
This is graph of function
and its inverse function
(where
e
is base of natural logarithm)
(1) Solve
(2) And, consider a line that passes through a point and is parallel with x axis. Let a point where this line intersects with curve be . Calculate area that is surrounded by x axis, y axis, curve , and line .
Let the answer of question (1) be X and the answer of question (2) be Y. Evaluate .
The answer is 2.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Apply natrual log on both side, ln x = ln e 2 x ∴ y = 2 1 ln x
Therefore, the inverse function of f ( x ) , the g ( x ) is
g ( x ) = 2 1 ln x
∴ lim x → 0 g ( 2 x + 1 ) f ( 2 x ) − 1 = lim x → 0 2 1 ln ( 2 x + 1 ) e 4 x − 1
= 2 lim x → 0 { 4 x e 4 x − 1 × ln ( 2 x + 1 ) 2 x × 2 4 }
= 4 lim x → 0 4 x e 4 x − 1 × lim x → 0 ln ( 2 x + 1 ) 2 x 1 1
= 4 × 1 × 1
4 = X
f ( k ) = e 2 k = 4
∴ k = 2
Since f ( a ) = 2
e 2 a = 2
∴ a = 2 1 ln 2
Therefore the area we want to evaluate is
∫ 0 2 1 ln 2 e 2 x d x = [ 2 1 e 2 x ] 0 2 1 ln 2
= 2 1 e ln 2 − 2 1
= 2 1 × 2 − 2 1
2 1 = Y