Magnetism + Calculus + Mechanics = Megatulics
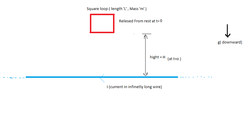 Let an
Super Conducting
Square Loop ( having negligible resistance ) and has Self inductance "L" and has mass of "m"
and side length
l
is released from rest in the gravity from the height "H" at time
t=0.There is an infinitely Long current carrying wire which is in Same Plane of that of Square Loop and current
I
0
flowing in it.
Let an
Super Conducting
Square Loop ( having negligible resistance ) and has Self inductance "L" and has mass of "m"
and side length
l
is released from rest in the gravity from the height "H" at time
t=0.There is an infinitely Long current carrying wire which is in Same Plane of that of Square Loop and current
I
0
flowing in it.
Then Find The Velocity of the square loop when it is at height of 4 H from the wire.
Details and assumptions
∙ m = 1 k g ∙ L = 1 0 h e n r y ∙ l = 1 m ∙ I 0 = 1 0 7 A m p . ∙ H = 2 m ∙ g = 9 . 8 m / s 2 .
This is Original
This is Part of this Set Mixing of Concepts
The answer is 5.439.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
It could have been much easier if you had used conservation of energy. The answer is 3 g l − 4 π 2 m L ( μ 0 I 0 l ln 2 ) 2 = 5 . 4
Use
2 1 m v 2 = m g ∗ 3 H / 4 − 2 1 L i 2
Log in to reply
how will u get the value of current in your equation for conservation of energy
i think the effect of magnetic force is negligible since by simple conservation of energy result= sqrt(3gh/2)=5.42m/s
@Deepanshu Gupta your pain is nothing compared to mine , i spent 1 hour on it(solving+writing monstrous latex!), i read it wrong , i thought you want time to be calculated , OH MAN ! when i read you want velocity , my face just brightened up and smile prevailed over it :P now for the solution , d t 2 d 2 h = g − F m a g . here the current can be calculated as d ϕ = d i * \L and then the force on current formula can be used , just to check you can see what F m a g . comes , it would be { I }_{ ind }\quad = \frac { { \mu }_{ 0 }{ I }_{ 0 }l }{ 2\pi L } \ln { \frac { 2(y+l) }{ 3y } \times \frac { { \mu }_{ 0 }{ I }_{ 0 } }{ 2\pi } (\frac { 1 }{ y } \quad -\quad \frac { 1 }{ y+l) } , this can be equated to m d x d v , so , you were saved of that cumbersome double integral , you would have had to calculate ! :P thanks god !
Well Now I feel very Tired Since It Takes approximately my 45 minutes to post it on brilliant. Anyway Solution Begins Here :
Let any time t=t net induced emf in is ' E i n d ' So
E i n d = I i n d R .
Now Loop Is Super Conducting So R ≈ 0 .
⇒ E i n d = 0 .
So according To Faraday's Law of induction.
⇒ d t − d ϕ m = 0 .
∴ ϕ m , n e t , a t t = t = ϕ m , n e t , a t t = 0 ∵ ϕ n e t = ϕ e x t e r n a l m a g . f i e l d + ϕ s e l f c u r r e n t .
Now Let at time t=t current in loop is I i n d And Loop is at an height of y from the wire So Flux produced due to Self induction Phenomena will be :
( ϕ s e l f c u r r e n t ) t = t = L × I i n d ⟶ ( 1 ) .
Now For Calculating Flux from external magnetic field( mag. field of infinite wire) will be calculated by considering Rectangular strip ( green coloured shown in figure) of length ' l ' and width dr which is at an height of ' r ' And at that instant of time Loop is at an height of y from wire :
( ϕ e x t e r n a l m a g . f i e l d ) t = t = ∫ r = y r = y + l B e x t . d A cos π = − ∫ r = y r = y + l 2 π r μ 0 I 0 . l d r = − 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ln y y + l ⟶ ( 2 ) .
Now net flux is constant So :
∵ ϕ m , n e t , a t t = t = ϕ m , n e t , a t t = 0 ⇒ L I i n d − 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ln y y + l = − 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ln 2 l 2 l + l ⇒ L I i n d − 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ln y y + l = − 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ln 2 3 ⇒ I i n d = 2 π L μ 0 I 0 l ln 3 y 2 ( y + l ) ⟶ ( 3 ) .
Now Draw FBD of the loop at that instant of time. and use Newtons laws of motion
F n e t = m × a n e t .
And You will see That net magnetic Force will acts in upwards and gravitational force in downward Direction.
m g − F m a g = m ( − d y v d v ) .
Here I used the fact that
a = − d x v d v ( ∵ y ↓ e s w i t h v ↑ e s ) .
So
m g − ( I i n d × l × B e x t ) = − m d x v d v m g − ( I i n d × l × 2 π μ 0 I 0 ( y 1 − y + l 1 ) = − m d x v d v .
Now Put all values which we have calculated already So the Differential equation becomes:
Note
here in solution I used frequently that
H=2 l
You check this according to data given in question.
( 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ) 2 m L 1 ∫ y = 2 l y = l / 2 ( y 1 − y + l 1 ) ln 3 y 2 ( y + l ) d y − g ∫ y = 2 l y = l / 2 d y = ∫ 0 v v d v .
Consider the integral E = ∫ y = 2 l y = l / 2 ( y 1 − y + l 1 ) ln 3 y 2 ( y + l ) d y .
Now Substitute the ln 3 y 2 ( y + l ) = z .
So this integral converts into :
( − ∫ z d z = − 2 z 2 = − 2 ( ln 3 y 2 ( y + l ) ) 2 ⇒ E = − ⎣ ⎡ 2 ( ln 3 y 2 ( y + l ) ) 2 ⎦ ⎤ 2 l l / 2 ⇒ E = 2 − ( ln 2 ) 2 .
So putting this integral in original equation we get an simply integrate The Rest part we get velocity
v = 3 g l − ( 2 π μ 0 I 0 l ) 2 m L ( ln 2 ) 2 .
Now put the Values we get answer i.e
v = 5 . 4 m \s .
Q.E.D