Mathematics Q6
∫ 0 1 x 2 − x + 1 arcsin x d x
If the integral above is equal to n π 2 , find n .
This Question is Part of My Mathematics Set
The answer is 108.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Rather than substitution directly apply a+b-x property and use the formula of arcsina+arcsinb to get the integral of 1/x^2-x+1
I = ∫ 0 1 1 − x ( 1 − x ) arcsin ( x ) d x I = ∫ 0 1 1 − x ( 1 − x ) arcsin ( 1 − x ) d x 2 I = ∫ 0 1 1 − x ( 1 − x ) arcsin ( x ) + arcsin ( 1 − x ) d x arcsin ( x ) + arcsin ( 1 − x ) = arcsin ( sin ( arcsin ( x ) + arcsin ( 1 − x ) ) ) = arcsin ( sin ( arcsin ( x ) ) cos ( arcsin ( 1 − x ) ) + sin ( arcsin ( 1 − x ) ) cos ( arcsin ( x ) ) ) = arcsin ( x + 1 − x ) = 2 π I = 4 π ∫ 0 1 1 − x ( 1 − x ) 1 d x = 4 π ∫ 0 1 ( x − 1 / 2 ) 2 + 3 / 4 1 d x = 4 π 3 2 arctan ( 3 2 ( x − 1 ) ) ∣ 0 1 = 6 3 π 2 = 1 0 8 π 2
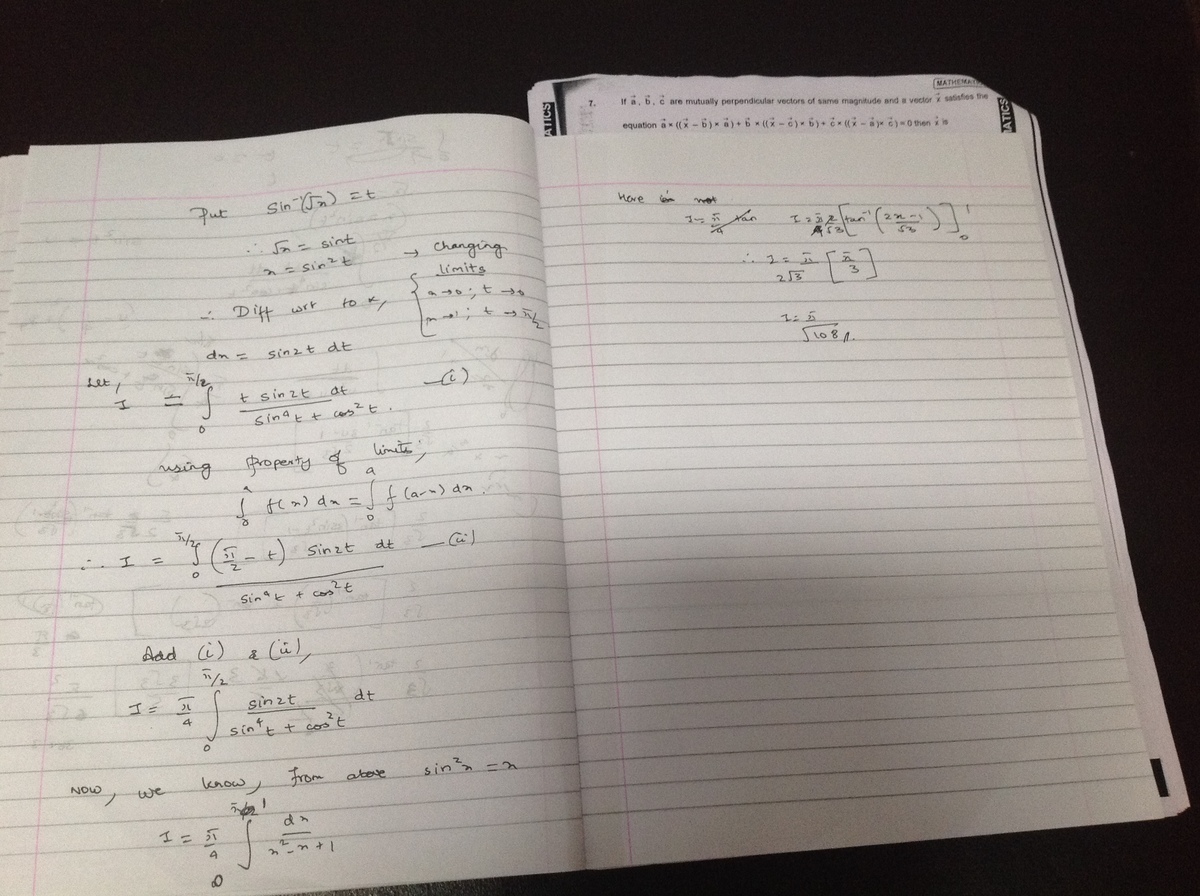
Similar method with Akhil Jain 's
I = ∫ 0 1 x 2 − x + 1 arcsin x d x = ∫ 0 2 π sin 4 θ − sin 2 θ + 1 2 θ sin θ cos θ d θ = 2 1 ∫ 0 2 π sin 4 θ − sin 2 θ + 1 2 θ sin θ cos θ + cos 4 θ − cos 2 θ + 1 2 ( 2 π − θ ) cos θ sin θ d θ = 2 1 ∫ 0 2 π sin 4 θ − sin 2 θ + 1 2 θ sin θ cos θ + sin 4 θ − sin 2 θ + 1 ( π − 2 θ ) sin θ cos θ d θ = 2 π ∫ 0 2 π sin 4 θ − sin 2 θ + 1 sin θ cos θ d θ = 2 π ∫ 0 1 u 4 − u 2 + 1 u d u = 4 π ∫ 0 1 t 2 − t + 1 1 d t = 4 π ∫ 0 1 ( t − 2 1 ) 2 + 4 3 1 d t = 3 π ∫ 0 1 3 4 ( t − 2 1 ) 2 + 1 1 d t = 2 3 π ∫ − 3 1 3 1 v 2 + 1 1 d v = 2 3 π tan − 1 v ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ − 3 1 3 1 = 6 3 π 2 = 1 0 8 π 2 Let sin θ = x , sin 2 θ = x , d x = 2 sin θ cos θ d θ Using ∫ a b f ( x ) d x = ∫ a b f ( a + b − x ) d x Let u = sin θ , d u = cos θ d θ Let t = u 2 , d t = 2 u d u Let v = 3 2 ( t − 2 1 ) , d v = 3 2 d t
⟹ n = 1 0 8