Molecular orbital theory
Is B 2 Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic?
- Note
- B represents Boron
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
B 2 is paramagnetic because it has two unpaired electrons..
DUE TO 2S-2P MIXING !
The mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals results in increase in energy of the σ 2 p orbital and lowering of σ 2 s orbital.... Right?
Log in to reply
ya occur in species in which electrons r <14
From the Molecular Orbital diagram, we can see that there is one one electron in both of the π Bonds which results in Paramagnetic.
σ
1
s
2
σ
∗
1
s
2
σ
2
s
2
σ
∗
2
s
2
π
2
p
1
π
∗
2
p
1
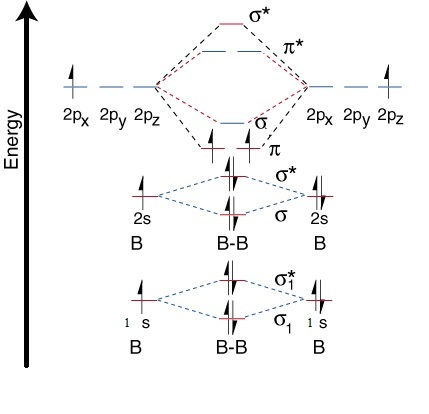 MOT Diagram
MOT Diagram
It's configuration is σ 1 s 2 σ 1 s 2 ∗ σ 2 s 2 σ 2 s 2 ∗ π 2 p 1 π 2 p 1