Tongue Rolling
Given that the ability to roll a tongue is a dominant trait, if a heterozygous tongue-roller marries a non-tongue roller , what is the probability that their child is a non-tongue roller ?
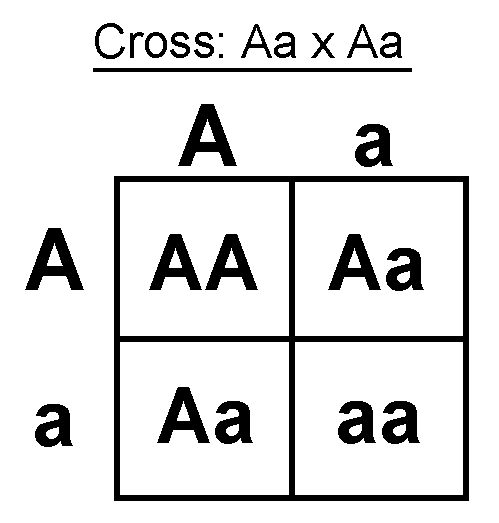
Punnett squares are used to estimate the probability of inheriting a certain gene by crossing the alleles from both parents. A capitalized letter is used to show a dominant trait while a non-capitalized letter shows a recessive trait. Here's an example:
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
As Steven is heterozygous for the particular trait, his genes must be of the form Xx . And as Natalie must be having homozygous recessive condition as she can't roll her tongue hence it should be xx . Now let's draw a punnet square:
x x X Xx Xx x xx xx
From the table, we can easily deduce that the probability of their child being a non-roller is 5 0 %