More of a project than a problem - Part 2
A cuboid measures 2 × 3 × 5 . Find the surface area of revolution that results when the cuboid is rotated about its space diagonal (a space diagonal is a line segment connecting two opposite vertices such that the center of the cuboid bisects it). The use of a programming environment is highly recommended.
The answer is 122.727.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Thanks for a great solution. Happy New Year to you.
This one makes use of much of the machinery of the previous problem. The differences are at the end. Here is my process:
Let the space diagonal be between points ( 0 , 0 , 0 ) and ( 2 , 3 , 5 ) . Let u be a unit vector along the space diagonal, and let u 1 and u 2 be unit vectors perpendicular to u .
Let the parameter α be the distance along the space diagonal. Let the value σ be the perpendicular distance from a point on the space diagonal to some place on the cuboid. Let θ be an angular parameter.
u 3 = c o s θ u 1 + s i n θ u 2 Point on Cuboid Surface = α u + σ u 3
Now, the tricky part is that for each α , θ varies continuously between 0 and 2 π . Consequently, there are infinitely many σ values for each α . The processing is as follows:
1)
For every
α
between
0
and the length of the space diagonal (in small steps), sweep
θ
from
0
to
2
π
in small steps.
2)
For every
θ
, form
u
3
and determine a
σ
value corresponding to the intersection with the infinite plane containing each cuboid face. There will be six
σ
calculations in total.
3)
The intersection point with the cuboid corresponds to the smallest positive
σ
value. Call this
σ
i
n
t
e
r
s
e
c
t
4)
For each
α
, as
θ
is swept, keep track of the largest value of
σ
i
n
t
e
r
s
e
c
t
. Call this
σ
m
a
x
This is where the old solution ends and the new solution begins
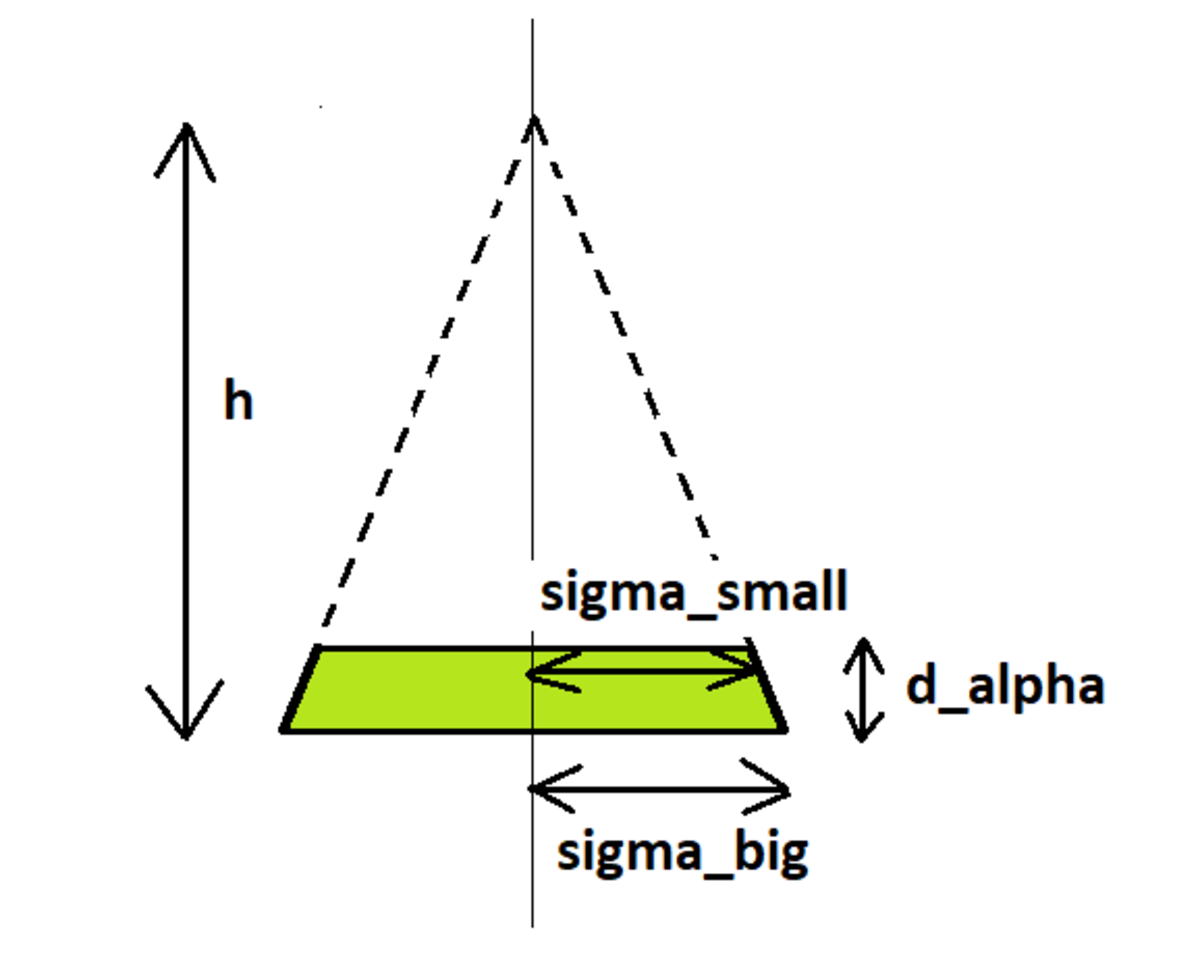
5 ) Every time we increment α , we need to calculate a new value of σ m a x and construct a partial cone according to the diagram below. We have to use the new value of σ m a x and the old (stored) value of σ m a x to do this.
6)
Call the larger value of the two
σ
b
i
g
and the smaller value
σ
s
m
a
l
l
.
7)
Find the height of the cone from the proportionality
σ
b
i
g
−
σ
s
m
a
l
l
d
α
=
σ
b
i
g
h
8)
The surface area of the "cone slice" is equal to the lateral surface area of the total cone of height
h
, minus the lateral surface area of the smaller cone of height
h
−
d
α
.
9)
The slant heights of the two cones are
h
2
+
σ
b
i
g
2
and
(
h
−
d
α
)
2
+
σ
s
m
a
l
l
2
10)
The surface areas of the two cones are
π
σ
b
i
g
h
2
+
σ
b
i
g
2
and
π
σ
s
m
a
l
l
(
h
−
d
α
)
2
+
σ
s
m
a
l
l
2
11)
The infinitesimal surface area is
π
σ
b
i
g
h
2
+
σ
b
i
g
2
−
π
σ
s
m
a
l
l
(
h
−
d
α
)
2
+
σ
s
m
a
l
l
2
12)
Adding up all of the infinitesimal surface areas of the partial cones yields a total surface area of revolution of about
1
2
2
.
7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 |
|
Using the following code, the result for a = 2 , b = 3 , and c = 5 is S ≈ 1 2 2 . 7 2 7 .