Mutual I’m Sure
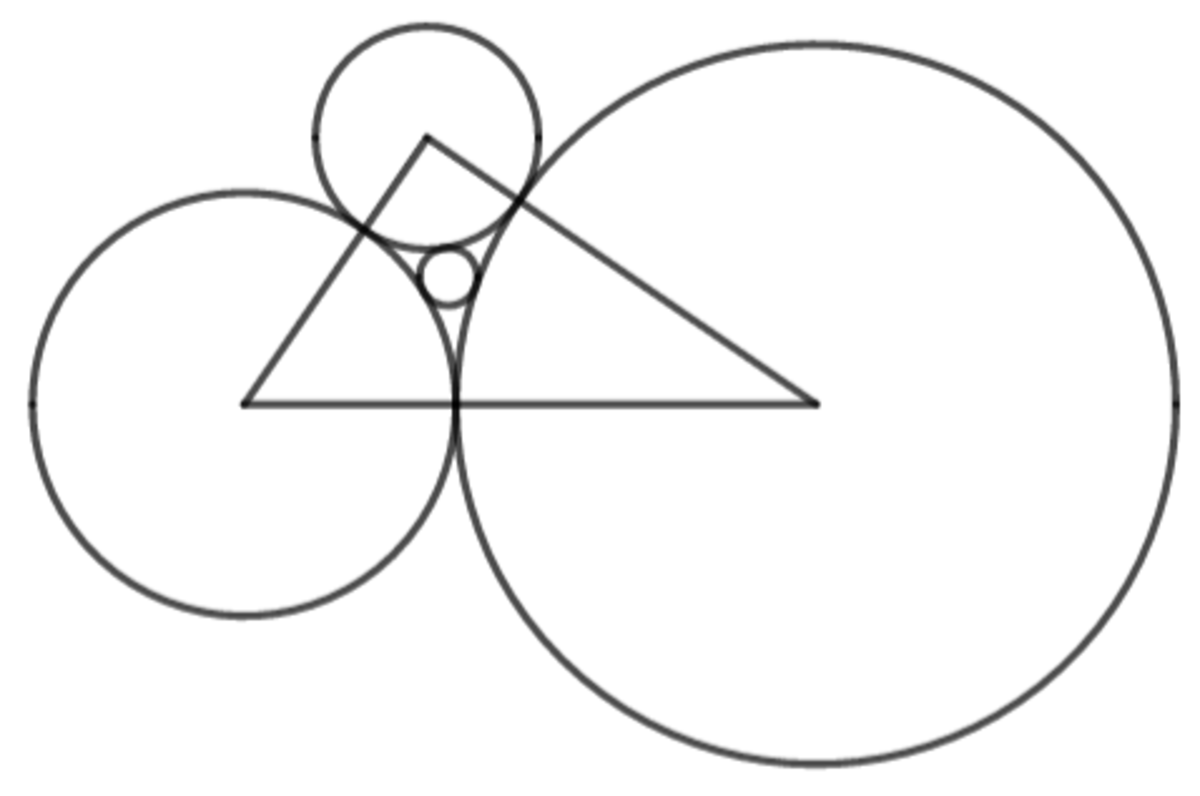
The centers of the three exterior circles of four mutually tangent circles are connected to form a right triangle with a perimeter of 3 2 9 . If the radius of the interior circle and the area of the triangle are also both integers, find the area of the triangle.
The answer is 4418.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
@David Vreken - phewf, great problem but tough!! I was really surprised at the result T = u above - I bet there's a better way to get to that geometrically.
Is this anything like your approach? Or did I miss a shortcut?
Log in to reply
If the sides of the triangle are a 2 = a + b , b 2 = a + c , and c 2 = b + c , and the semiperimeter is s = 2 1 ( a 2 + b 2 + c 2 ) = a + b + c , and a = a + b + c − ( b + c ) = s − c 2 , b = a + b + c − ( a + c ) = s − b 2 , and c = a + b + c − ( a + b ) = s − a 2 , which is useful for applying Heron's formula T = s ( s − a 2 ) ( s − b 2 ) ( s − c 2 ) . This fact help me simplify Descartes's circle theorem, although it was still pretty long and I'm not sure if it was a better approach than yours.
With a bit of hunting on the encyclopedia of triangle centres it turns out the centre of the small circle is the equal detour point .
Log in to reply
Thanks! I was trying to see if there was a name for it earlier but couldn't find it.
Log in to reply
Finding things in the ETC is a bit of a puzzle in itself. The small circle is the "inner Soddy circle" of the triangle, although that seems to be just another way of describing the tangent circles. The detour thing is quite a surprise.
Let the radii of the three exterior circles be r 1 , r 2 , and r 3 , so that the legs of the right triangle are a = r 1 + r 2 and b = r 1 + r 3 and the hypotenuse is c = r 2 + r 3 .
The semiperimeter is then s = 2 1 ( a + b + c ) = 2 1 ( ( r 1 + r 2 ) + ( r 1 + r 3 ) + ( r 2 + r 3 ) ) = r 1 + r 2 + r 3 , so s − a = ( r 1 + r 2 + r 3 ) − ( r 1 + r 2 ) = r 3 .
Similarly, s − b = r 2 and s − c = r 1 .
The semiperimeter is also half the perimeter, so s = 2 1 P = 2 3 2 9 .
By Heron's formula the area of the triangle is T = s ( s − a ) ( s − b ) ( s − c ) . Substituting s , s − a , s − b , and s − c from above gives T = 2 3 2 9 r 1 r 2 r 3 , and rearranging gives r 1 r 2 r 3 = 3 2 9 2 T 2 .
By the Pythagorean Theorem, ( r 1 + r 2 ) 2 + ( r 1 + r 3 ) 2 = ( r 2 + r 3 ) 2 , which rearranges to r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 = 2 r 2 r 3 − r 1 2 .
By the area of the triangle equation, T = 2 1 ( r 1 + r 2 ) ( r 1 + r 3 ) , which rearranges to r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 = 2 T − r 1 2 .
That means 2 T = r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 + r 1 2 = 2 r 2 r 3 , so T = r 2 r 3 .
Substituting T = r 2 r 3 into r 1 r 2 r 3 = 3 2 9 2 T 2 gives r 1 = 3 2 9 2 T .
Substituting r 1 = 3 2 9 2 T into r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 = 2 T − r 1 2 gives r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 = 2 T − 3 2 9 2 4 T 2
By Descartes' Theorem , the reciprocal of the radius d of the interior circle is d 1 = r 1 1 + r 2 1 + r 3 1 + 2 r 1 r 2 1 + r 1 r 3 1 + r 2 r 3 1 .
This rearranges to d = r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 + 2 ( r 1 + r 2 + r 3 ) r 1 r 2 r 3 r 1 r 2 r 3 .
Substituting r 1 + r 2 + r 3 = 2 3 2 9 , r 1 r 2 r 3 = 3 2 9 2 T 2 , and r 1 r 2 + r 1 r 3 + r 2 r 3 = 2 T − 3 2 9 2 4 T 2 into d gives d = 2 T − 3 2 9 2 4 T 2 + 2 2 3 2 9 ⋅ 3 2 9 2 T 2 3 2 9 2 T 2 = 2 ( 3 2 9 2 − T ) 3 2 9 T .
The equation d = 2 ( 3 2 9 2 − T ) 3 2 9 T can be rearranged to ( 3 2 9 2 − T ) ( 2 d + 3 2 9 ) = 3 2 9 3 .
Therefore, both 3 2 9 2 − T and 2 d + 3 2 9 are positive factors of 3 2 9 3 , so 3 2 9 2 − T > 0 , or T < 3 2 9 2 .
Let f be the factor of 3 2 9 3 such that f = 3 2 9 2 − T > 0 . Then T = 3 2 9 2 − f , and since T is positive, f < 3 2 9 2 , or f < 1 0 8 2 4 1 .
Now for a right triangle, P = a + b + a 2 + b 2 and T = 2 1 a b . Solving for a in terms of P and T gives a = 4 P 1 ( P 2 + 4 T ± P 4 − 2 4 P 2 T + 1 6 T 2 ) , so from the discriminant P 4 − 2 4 P 2 T + 1 6 T 2 > 0 we know that either T < 4 1 ( 3 − 2 2 ) P 2 or T > 4 1 ( 3 + 2 2 ) P 2 .
So for P = 3 2 9 , either T < 4 1 ( 3 − 2 2 ) 3 2 9 2 or T > 4 1 ( 3 + 2 2 ) 3 2 9 2 . However, since T < 3 2 9 2 , T ≯ 4 1 ( 3 + 2 2 ) 3 2 9 2 , so T < 4 1 ( 3 − 2 2 ) 3 2 9 2 . In other words, T < 4 6 4 3 .
Since T = 3 2 9 2 − f , that means 3 2 9 2 − f < 4 6 4 3 , and this solves to 1 0 3 5 9 8 < f .
Therefore, 1 0 3 5 9 8 < f < 1 0 8 2 4 1 . Testing the ( 3 + 1 ) ( 3 + 1 ) = 1 6 possible factors of 3 2 9 3 = 7 3 4 7 3 ( 1 , 7 , 4 7 , 4 9 , 3 2 9 , 3 4 3 , 2 2 0 9 , 2 3 0 3 , 1 5 4 6 3 , 1 6 1 2 1 , 1 0 3 8 2 3 , 1 0 8 2 4 1 , 7 2 6 7 6 1 , 7 5 7 6 8 7 , 5 0 8 7 3 2 7 , and 3 5 6 1 1 2 8 9 ), only 1 0 3 8 2 3 is within this range, so f = 1 0 3 8 2 3 .
Therefore, T = 3 2 9 2 − f = 3 2 9 2 − 1 0 3 8 2 3 = 4 4 1 8 .
Also:
d = 2 ( 3 2 9 2 − T ) 3 2 9 T = 2 ( 3 2 9 2 − 4 4 1 8 ) 3 2 9 ⋅ 4 4 1 8 = 7
a = 4 P 1 ( P 2 + 4 T − P 4 − 2 4 P 2 T + 1 6 T 2 ) = 4 ⋅ 3 2 9 1 ( 3 2 9 2 + 4 T − 3 2 9 4 − 2 4 ⋅ 3 2 9 2 ⋅ 4 4 1 8 + 1 6 ⋅ 4 4 1 8 2 ) = 2 8 4 7 ( 5 7 − 1 1 3 )
b = 4 P 1 ( P 2 + 4 T + P 4 − 2 4 P 2 T + 1 6 T 2 ) = 4 ⋅ 3 2 9 1 ( 3 2 9 2 + 4 T + 3 2 9 4 − 2 4 ⋅ 3 2 9 2 ⋅ 4 4 1 8 + 1 6 ⋅ 4 4 1 8 2 ) = 2 8 4 7 ( 5 7 + 1 1 3 )
c = a 2 + b 2 = ( 2 8 4 7 ( 5 7 − 1 1 3 ) ) 2 + ( 2 8 4 7 ( 5 7 + 1 1 3 ) ) 2 = 1 4 1 9 2 7
r 1 = s − c = 2 3 2 9 − 1 4 1 9 2 7 = 7 1 8 8
r 2 = s − b = 2 3 2 9 − 2 8 4 7 ( 5 7 + 1 1 3 ) = 2 8 4 7 ( 4 1 − 1 1 3 )
r 3 = s − a = 2 3 2 9 − 2 8 4 7 ( 5 7 − 1 1 3 ) = 2 8 4 7 ( 4 1 + 1 1 3 )
Let the radii of the three outer circles be a < b < c , so that the sides of the right-angled triangle are a + b , a + c and b + c . Let P = 3 2 9 be the perimeter of this triangle; let T be its area; and let r be the radius of the interior circle. We're told that r and T are integers; and we want to find T .
The idea will be to find a relationship between r , P and T by eliminating a , b , c from various equations. (This is useful as we don't know if a , b , c are integers or not.)
Adding up the sides, 2 ( a + b + c ) = P
By Pythagoras, ( a + b ) 2 + ( a + c ) 2 = ( b + c ) 2 ⇒ a ( a + b + c ) = b c
Using the expression for the perimeter, this is a P = 2 b c
The area of the triangle is T = 2 ( a + b ) ( a + c )
Now, the blue equations are symmetric in b and c (we can swap them without changing the equations). So, let u = b c and v = b + c ; the equations become 2 ( a + v ) = P a P = 2 u 2 T = a 2 + a v + u
We get v = 2 P − a and u = 2 a P ; substituting, 2 T = a 2 + a ( 2 P − a ) + 2 a P = a P
so a = P 2 T .
Plugging back in, we get u = T and v = 2 P − P 2 T .
By Descartes' circle theorem, r 1 = a 1 + b 1 + c 1 + b c 1 + c a 1 + a b 1
Substituting from above, things cancel out nicely to give r = 2 P 2 − 2 T P T
Rearranging, 2 r P 2 − 2 r T = P T
Note that, for a given perimeter, the largest right-angled triangle is an isosceles one, with area T max = 4 1 ( 3 − 2 2 ) P 2 . In this case, that's around 4 6 4 2 . 8 .
The only integer solution to the final equation satisfying this constraint is r = 7 and T = 4 4 1 8 .