Not A Telescoping Sum
k = 1 ∑ ∞ ( 3 k − 1 1 − 3 k 1 )
The above sum has a closed form of B ln A − D 2 E π C where A , B , C , D and E are positive prime numbers. Find the value of A + B + C + D + E .
The answer is 13.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Good approach
Interesting idea! Very simple and elegant solution.
same method! :)
S = k = 1 ∑ ∞ ( 3 k − 1 1 − 3 k 1 ) = k = 1 ∑ ∞ 3 k 2 sin ( ( k − 1 ) 3 2 π ) See Note. = ℑ [ 3 2 e − i 3 2 π k = 1 ∑ ∞ k e i 3 2 k π ] = ℑ [ − 3 2 e − i 3 2 π ln ( 1 − e i 3 2 π ) ] = ℑ [ − 3 2 ( − 2 1 − i 2 3 ) ln ( 2 3 − i 2 3 ) ] = ℑ [ ( 3 1 + i ) ln ( 3 ( 2 3 − i 2 1 ) ) ] = ℑ [ ( 3 1 + i ) ln ( 3 e − i 6 π ) ] = ℑ [ ( 3 1 + i ) ( 2 ln 3 − i 6 π ) ] = 2 ln 3 − 1 8 3 π
⇒ a + b + c + d + e = 3 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 2 = 1 3
Note:
S = k = 1 ∑ ∞ ( 3 k − 1 1 − 3 k 1 ) = 2 1 − 3 1 + 5 1 − 6 1 + 8 1 − 9 1 + . . . = 1 0 + 2 1 − 3 1 + 4 0 + 5 1 − 6 1 + 7 0 + 8 1 − 9 1 + . . . = 3 2 ( 0 ⋅ 1 1 + 2 3 ⋅ 2 1 − 2 3 ⋅ 3 1 + 0 ⋅ 4 1 + 2 3 ⋅ 5 1 − 2 3 ⋅ 6 1 + 0 ⋅ 7 1 + 2 3 ⋅ 8 1 − 2 3 ⋅ 9 1 + . . . ) = 3 2 ( sin 0 ⋅ 1 1 + sin 3 2 π ⋅ 2 1 − sin 3 4 π ⋅ 3 1 + sin 2 π ⋅ 4 1 + sin 3 8 π ⋅ 5 1 − sin 3 1 0 π ⋅ 6 1 + sin 4 π ⋅ 7 1 + sin 3 1 4 π ⋅ 8 1 − sin 3 1 6 π ⋅ 9 1 + . . . ) = k = 1 ∑ ∞ 3 k 2 sin ( ( k − 1 ) 3 2 π )
Can you explain how you got the second line?
Log in to reply
Try writing out the first few values in the first and second lines. You'll see they are the same sum.
Very clever solution! Good job!
Sir,I saw that you have solved my problem named 'Area' (of calculus section) correctly.It would be very helpful if you could share your proof or atleast provide a brief outline of your solution as I am unable to solve the question.
How did you got the second line ?
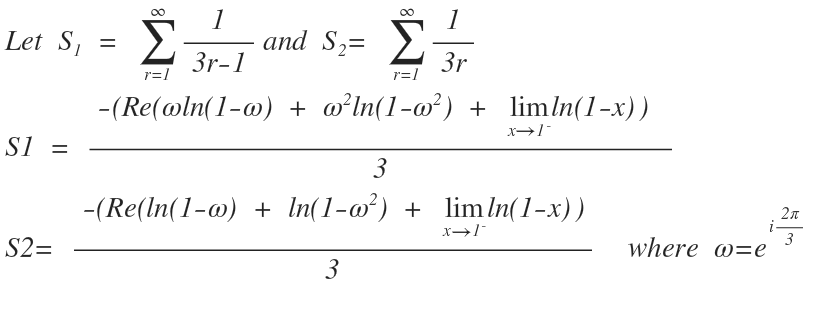
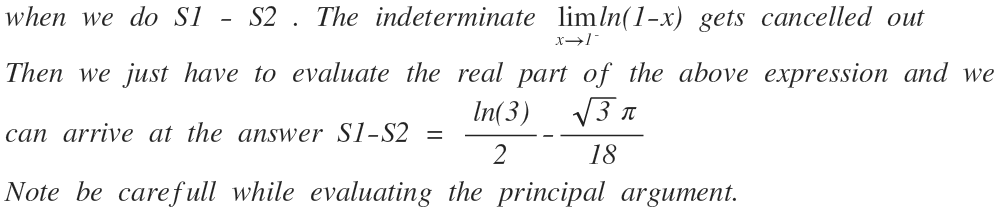
This is not a full solution . The calculation part is left for u guys. I have used taylor series and complex cube root of unity to solve the problem
Eto Boro korli keno ? Integration lagalei to hoto.
∑ k = 1 ∞ ( 3 k − 1 1 − 3 k 1 ) = ∑ k = 1 ∞ ∫ 0 1 ( x 3 k − 2 − x 3 k − 1 ) d x = ∫ 0 1 ∑ k = 1 ∞ ( x 3 k − 2 − x 3 k − 1 ) d x = ∫ 0 1 1 − x 3 x − x 2 d x = 2 l n ( 3 ) − ( 3 2 ) 2 3 Π