Not Nine Circles Theorem
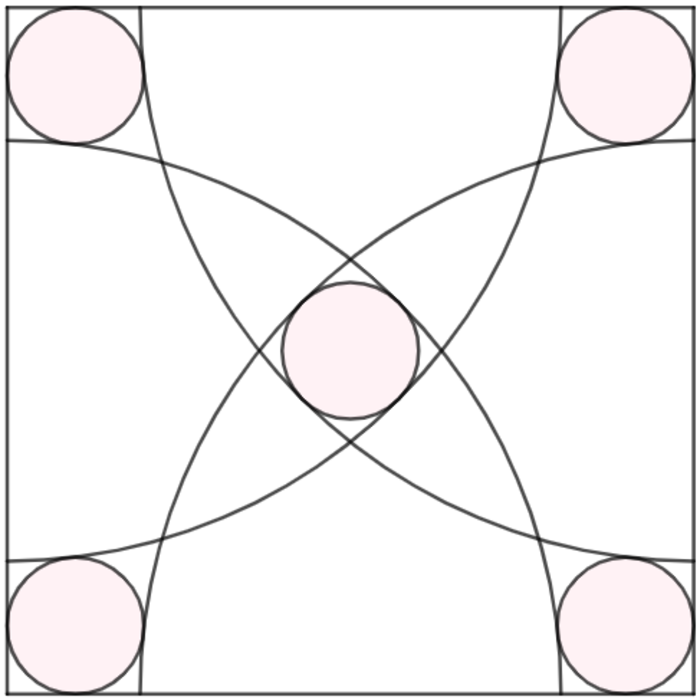
In the square, five identical pink circles and four quarter circles are positioned as shown. If the radius ratio of one quarter circle to one pink circle can be expressed as
A + B C + D E + F G
where A , B , C , D , E , F , and G are positive integers and C and G are square free. Input A + B + C + D + E + F + G as your answer.
The answer is 13.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Suppose the square has side 1, the large circles have radius R, the small circles have radius r. Half a diagonal is 2 1 2 = R − r We can also identify a right-angled tiangle with hypothenuse R+r and right sides 1-r and r so that ( R + r ) 2 = ( 1 − r ) 2 + r 2 Combining these we get 2 r 2 + ( 2 2 + 2 ) r − 4 1 = 0 Taking the positive root: r = 2 1 8 + 4 − 2 1 2 − 2 1 , R = 2 1 8 + 4 − 2 1
The ratio can, after some work, be reduced to r R = 3 + 2 + 2 2 + 2 Here we have A = 3 , B = 1 , C = 2 , D = 2 , E = 2 , F = 1 , G = 2 These numbers have sum of 1 3
In △ D E F , D E 2 ( 1 + r ) 2 ⟹ F D = E F 2 + F D 2 = 1 2 + F D 2 = r 2 + 2 r The length of each side of the square is, A D = A F + F D = 1 + r 2 + 2 r In △ D C B , D B = r + r − 2 , B C = 1 + r 2 + 2 r , C D = 1 + r 2 + 2 r D B 2 ( 2 r − 2 ) 2 ⟹ 2 r − 2 = B C 2 + C D 2 = ( 1 + r 2 + 2 r ) 2 + ( 1 + r 2 + 2 r ) 2 = 2 ( 1 + r 2 + 2 r ) Solving the above equation, we have r = 3 + 2 + 2 2 + 2 Therefore, A = 3 , B = 1 , C = 2 , D = 2 , E = 2 , F = 1 , G = 2 ⟹ A + B + C + D + E + F + G = 1 3