Now it gets hard
 So far we've understood that chaos stems from nearby paths diverging over time. A circle in the middle of the table will always cause nearby paths to diverge and hence that is the shape that makes the system chaotic.
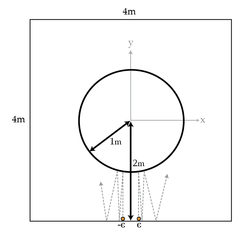
So far we've understood that chaos stems from nearby paths diverging over time. A circle in the middle of the table will always cause nearby paths to diverge and hence that is the shape that makes the system chaotic.
Let's do some quantitative analysis of the table with a circle. The circle in the middle is given by the equation . You start two (infinitesimally small) billiard balls at with a velocity purely in the positive y-direction. can be taken to be very small. What is the ratio of the distance apart the disks are after the 25th time they bounce off the side of the table to their distance after the 5th time they bounce off the side of the table? You may assume , but m.
The answer is 2.05E+15.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
0 solutions
No explanations have been posted yet. Check back later!