Oblique Cylinder 2
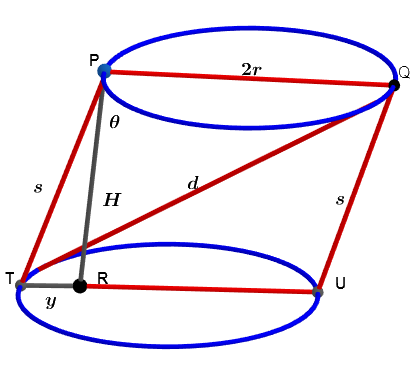
In the oblique cylinder above , is a parallelogram and is a right triangle. Let the volume and the lateral surface area of the oblique cylinder be and respectively, where is a positive real number.
- Find the value of the radius that minimizes the distance .
- Find the distance and find (in degrees).
If , find the value of to six decimal places.
The answer is 0.014067.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
V = π r 2 H = b 2 ⟹ H = π r 2 b 2 and A = 2 π r s = b ⟹ s = 2 π r b
⟹ Y ( r ) = y 2 ( r ) = s 2 ( r ) − H 2 ( r ) = π 2 b 2 ( 4 r 2 1 − r 4 b 2 ) ⟹ d r d Y = π 2 b 2 ( 2 r 5 8 b 2 − r 2 ) r > 0 ⟹ r = 2 2 b ⟹ s = 4 2 π 1 and H = 8 π 1 and y = s 2 − H 2 = 8 π 1 = H .
For 0 < b < 5 3 ⟹ d r 2 d 2 Y ∣ r = 2 2 b = 1 2 8 π 2 1 ( 3 − 5 b ) > 0 ⟹ min at r = 2 2 b .
Let m ∠ P T R = λ ⟹ cos ( λ ) = s ( r ) y ( r ) = 2 1 and θ = 1 8 0 − λ ⟹ cos ( θ ) = cos ( 1 8 0 − θ ) = − cos ( λ ) = − 2 1 ⟹ θ = 1 3 5 ∘
⟹ d 2 = s 2 + 4 r 2 + 4 r s cos ( λ ) = 3 2 π 2 1 + 3 2 b 2 + π 2 b = 3 2 π 2 3 2 2 π 2 b 2 + 3 2 2 π b + 1 ⟹ d = 4 2 π 3 2 2 π 2 b 2 + 3 2 2 π b + 1
d 2 = 3 2 π 2 3 2 2 π 2 b 2 + 3 2 2 π b + 1 = 2 π b ( 6 π b + 3 2 ) ⟹ 3 2 2 π 2 b 2 + 3 2 2 π b + 1 = 3 2 π 2 b ( 2 π 6 4 π b + 3 2 ) = 3 2 π 2 ( 3 2 b 2 + 2 π 3 2 b ) = 3 2 2 π 2 b 2 + 4 8 2 π b ⟹ 1 6 2 π b = 1 ⟹ b = 1 6 2 π 1 ≈ 0 . 0 1 4 0 6 7 .