Octagon inscribed in a rectangle.

An octagon with all equal sides is formed by cutting four congruent right triangles from each corner of the above rectangle with side lengths w and w − 2 .
Find the value of w for which the side length of the octagon is 5 1 − 5 .
The answer is 6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
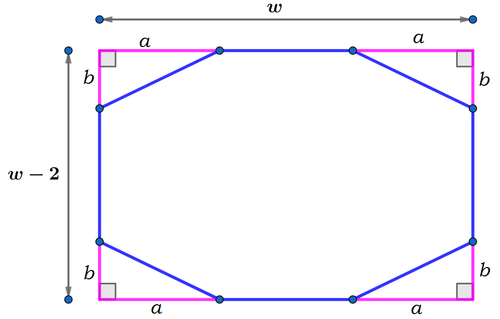
Let the side lengths of the legs of the right triangle cut off be a and b as seen. Then,
{ w = 2 a + 5 1 − 5 w − 2 = 2 b + 5 1 − 5 . . . ( 1 ) . . . ( 2 ) ⟹ ( 1 ) − ( 2 ) : 2 a − 2 b = 2 ⟹ b = a − 1
Note that:
a 2 + b 2 = ( 5 1 − 5 ) 2 2 a 2 − 2 a + 1 2 a 2 − 2 a − 7 5 + 1 0 5 1 = 7 6 − 1 0 5 1 = 0
The roots to the quadratic equation are a and b . By Vieta's formula, a + b = 1 . Let a = 2 1 + u and b = 2 1 − u , then
( 2 1 + u ) ( 2 1 − u ) ( u + 2 1 ) ( u − 2 1 ) u 2 − 4 1 u 2 ⟹ u ⟹ a ⟹ w = 2 1 0 5 1 − 7 5 = 2 7 5 − 1 0 5 1 = 2 7 5 − 1 0 5 1 = 4 1 5 1 − 2 0 5 1 = 2 1 0 − 5 1 = u + 2 1 = 2 1 1 − 5 1 = 2 a + 5 1 − 5 = 6
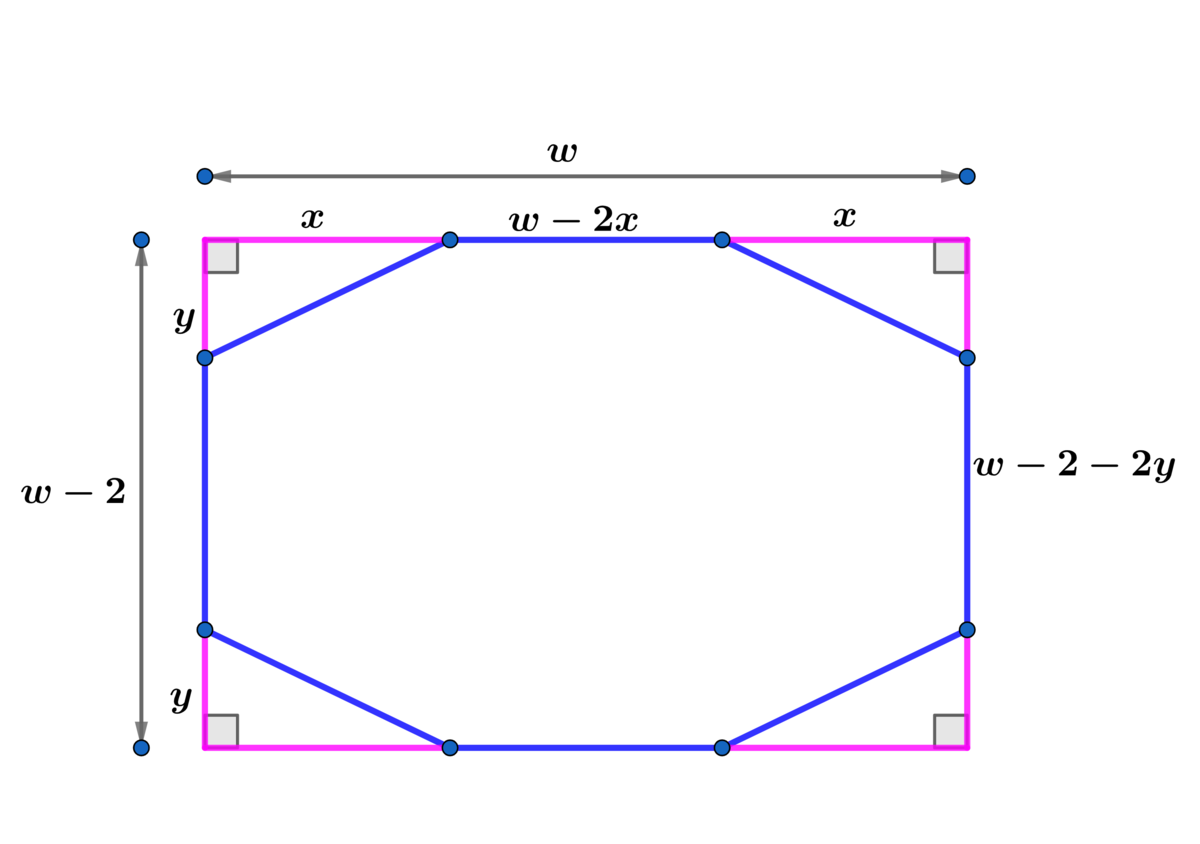
w − 2 x = w − 2 − 2 y ⟹ x − y = 1 ⟹ y = x − 1
and
x 2 + y 2 = ( w − 2 x ) 2 ⟹ x 2 + ( x − 1 ) 2 = w 2 − 4 w x + 4 x 2 ⟹
2 x 2 − 2 ( 2 w − 1 ) x + w 2 − 1 = 0 ⟹ x = 2 2 w − 1 ± 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3
Using x = 2 2 w − 1 + 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 ⟹ w − 2 x < 0 :
w − 2 x = 1 − w − 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 and ( 1 − w ) 2 − ( 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 ) =
− ( w 2 − 2 w + 2 ) < 0 for all real w
⟹ ∣ 1 − w ∣ < 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 ∴ we drop x = 2 2 w − 1 + 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3
and choose x = 2 2 w − 1 − 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 ⟹
w − 2 x = 1 − w + 2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 = 5 1 − 5 ⟹
2 w 2 − 4 w + 3 = ( ( 5 1 − 6 ) + w ) 2 = 8 7 − 1 2 5 1 + 2 ( 5 1 − 6 ) w + w 2 ⟹
w 2 + ( 8 − 2 5 1 ) w + 1 2 5 1 − 8 4 = 0 ⟹
w = 2 − 8 + 2 5 1 ± 2 1 5 1 − 2 0 5 1 = 2 − 8 + 2 5 1 ± 2 ( 1 0 − 5 1 ) 2 =
2 − 8 + 2 5 1 ± ( 1 0 − 5 1 ) = 6 , − 1 4 + 2 5 1
w = 2 5 1 − 1 4 ⟹ w − 2 < 0 ∴ choose w = 6
( 2 w − ( 5 1 − 5 ) ) 2 + ( 2 ( w − 2 ) − ( 5 1 − 5 ) ) 2 ⟹ w = ( 5 1 − 5 ) 2 = 6
Let the pink sides of the four right-angled triangles be a > b and the side of the octagon (given) be s , so that 2 a + s = w and 2 b + s = w − 2 . Also, by Pythagoras, a 2 + b 2 = s 2 .
Since we want to find w , we'll eliminate a and b . For convenience below, write x = w − s : 2 a 2 b 4 a 2 + 4 b 2 = x = x − 2 = x 2 + ( x − 2 ) 2 = 4 s 2
Tidying up and solving, x = 1 ± 2 s 2 − 1 . Clearly we can ignore the negative root; so we find w = s + 1 + 2 s 2 − 1 = 6
The simplest way to find s + 1 + 2 s 2 − 1 is by considering the quadratic that s solves; we have ( s + 5 ) 2 = 5 1 , which can be rewritten as s 2 = 2 6 − 1 0 s .
Now, 2 s 2 − 1 = 5 1 − 2 0 s = ( s + 5 ) 2 − 2 0 s = ( s − 5 ) 2 , and, noting that s < 5 , the rest is easy.