Preserving Sines
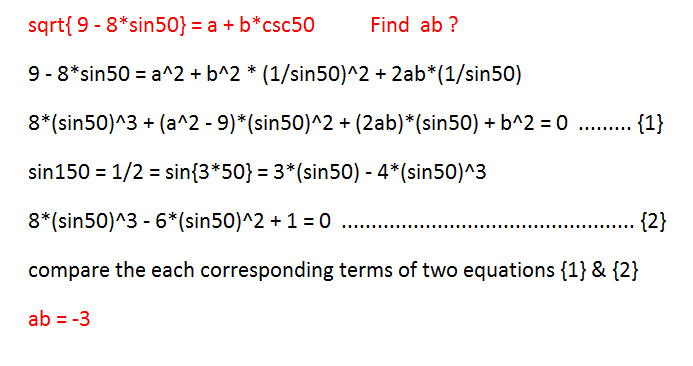
If , where and are integers, find .
Hint : You may need to use triple angle formula .
The answer is -3.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Relevant wiki: Sum and Difference Trigonometric Formulas - Problem Solving
Let y = 9 − 8 sin 5 0 ∘
So, y = sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) 9 sin 2 ( 5 0 ∘ ) − 8 sin 3 ( 5 0 ∘ ) = sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) 9 sin 2 ( 5 0 ∘ ) − 6 sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) + 6 sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) − 8 sin 3 ( 5 0 ∘ ) = sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) 9 sin 2 ( 5 0 ∘ ) − 6 sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) + 2 × sin ( 3 × 5 0 ∘ ) = sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) 9 sin 2 ( 5 0 ∘ ) − 6 sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) + 1 = sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) ∣ 3 sin ( 5 0 ∘ ) − 1 ∣ ⇒ a × b = − 3