Parabola Charge Stasis
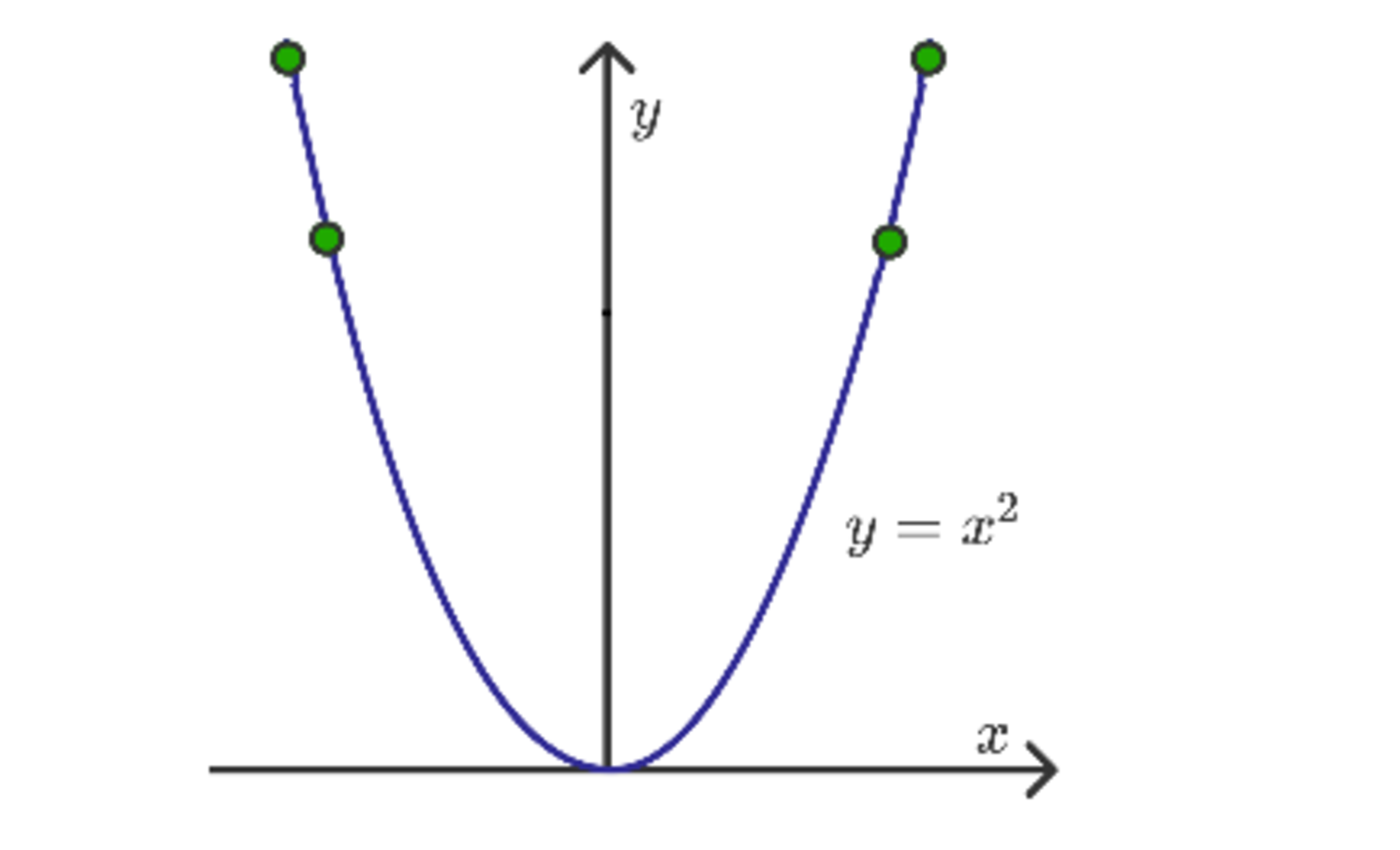
Four identical massless point-charges are placed on a section of wire in the shape of the curve , where .
If the charges are in stasis, what is the -coordinate of the charge closest to the origin (and to the right of the origin)?
Note: The charges can reside at the ends of the wire, but cannot leave the wire. The only force on the charges (other than the coulombic interactions) is from the wire itself.
The answer is 0.450162.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Since all the electrostatic forces on the outermost two particles will act to push these particles away from the centre, the outermost particles must be at the ends of the wires, and will therefore have coordinates ( − 1 , 1 ) and ( 1 , 1 ) . By symmetry, the inner two particles will have coordinates ( x , x 2 ) and ( − x , x 2 ) for some 0 < x < 1 .
We must minimize the electrostatic potential energy of the system, and hence must minimize V ( x ) = ( 1 − x ) x 2 + 2 x + 2 2 + ( 1 + x ) x 2 − 2 x + 2 2 + 2 x 1 + 2 1 (over 0 < x < 1 ), where V ( x ) is the sum of the reciprocals of the distances between the six pairs of particles. Handling this problem numerically, the minimum of V occurs when x = 0 . 4 5 0 1 6 2 .