Parity Blue and Yellow
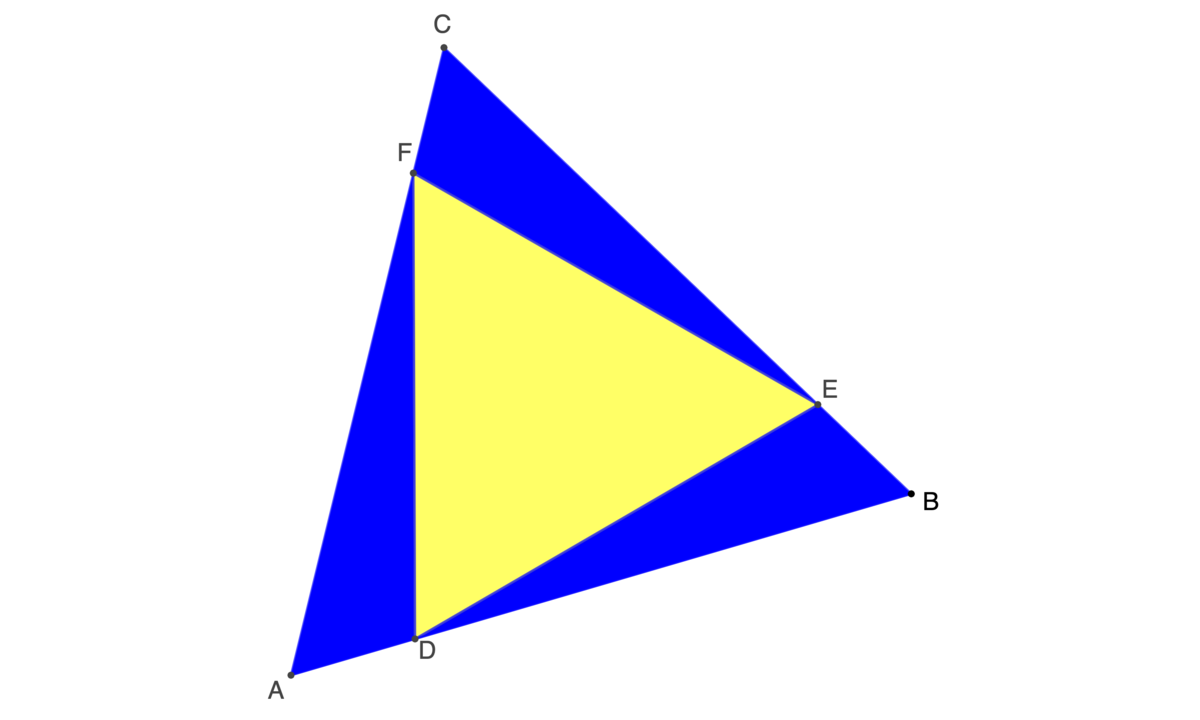
The figure shows a yellow equilateral triangle D E F is inscribed inside a larger equilateral triangle A B C with A B = 1 .
If the blue area is equal to the yellow area, find A D = x . There are two values of x . The smaller value of x is equal B A − A , where A and B are integers and A is square-free. Submit A + B .
The answer is 9.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Your latex math is broken. Hard to read :)
Let x denote the length of segment A D . So, we have, A D = B E = C F = x and A F = B D = C E = 1 − x Using the Cosine Rule , in △ A F D , D F 2 ∴ D F = A D 2 + A F 2 − 2 ⋅ A D ⋅ A F ⋅ cos ∠ D A F = x 2 + ( 1 − x ) 2 − 2 ⋅ x ⋅ ( 1 − x ) ⋅ cos 6 0 ∘ = 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 = F E = E D = 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 Yellow Area Yellow Area + Blue Area 2 ⋅ Yellow Area 2 ( 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 ) 3 6 x 2 − 6 x + 1 ∴ x = area ( △ D E F ) = D F 2 ⋅ 4 3 = 4 ( 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 ) 3 = area ( △ A B C ) = A B 2 ⋅ 4 3 = 4 3 = 0 = 6 3 ± 3 Therefore, x min = 6 3 − 3 ⟹ A = 3 , B = 6 ⟹ A + B = 9
Alternative: Blue Area = 3 ⋅ area ( △ A D F ) = 3 ⋅ 2 1 ⋅ A D ⋅ A F ⋅ sin ∠ A F D = 2 3 ⋅ x ⋅ ( 1 − x ) ⋅ sin 6 0 ∘ = 4 ( 3 x − 3 x 2 ) 3 Since Yellow Area = Blue Area , 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 = 3 x − 3 x 2 ⟺ 6 x 2 − 6 x + 1 = 0 ⟺ x = 6 3 ± 3
Note: A simple angle chase leads to ∠ A F D = ∠ B D E = ∠ C E F , which combined with ∠ A = ∠ B = ∠ C = 6 0 ∘ and D F = F E = E D implies that △ A D F ≅ △ C F E ≅ △ B D E .
AD = x = BE = CF so AF = 1 – FC = 1 – x.
1 blue area
= (1/2) × x × (1 – x) × sin 60°
= (Equal division of 3 blue area) × (Equal division of yellow-blue area) × (Full area)
= (1/3) × (1/2) × (1/2) × 1² × sin 60°
x (1 – x) = 1/6
x (x – 1) = –1/6
(x – 1/2)² = (1/2)² – (1/6) = 1/12
x = 1/2 ± 1/√12
= (√3 ± 1) / √12
= (3 ± √3) / 6
Answer = 3 + 6 = 9
When the blue area is equal to the yellow area, it means that the area of equilateral △ D E F is half that of equilateral t r i a n g l e A B C . This means that the side length of △ D E F , D E = 2 1 . By cosine rule :
E B 2 + D B 2 − 2 E B ⋅ D B ⋅ cos B x 2 + ( 1 − x ) 2 − 2 x ( 1 − x ) cos 6 0 ∘ 3 x 2 − 3 x + 2 1 x = D E 2 = 2 1 = 0 = 6 3 ± 9 − 6 = 6 3 − 3 Note that E B = A D = x Choosing the smaller value
The required answer A + B = 3 + 6 = 9 .