Partitioned Triangle
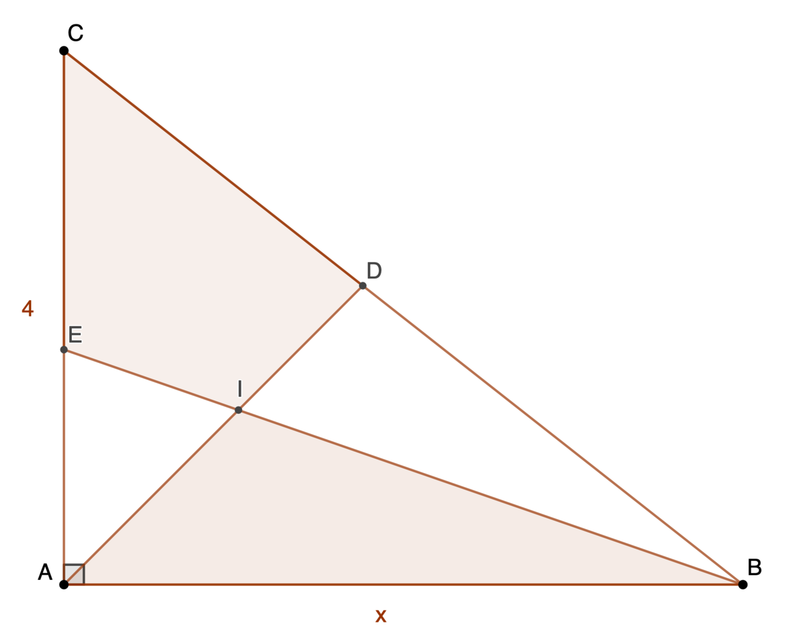
△ A B C has its incenter at I , ∠ A = 9 0 ∘ , A C = 4 , and A B = x . If the area of quadrilateral E I D C and the area of △ A I B are the same, find ⌊ 1 0 4 x ⌋ .
The answer is 50880.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Well done!
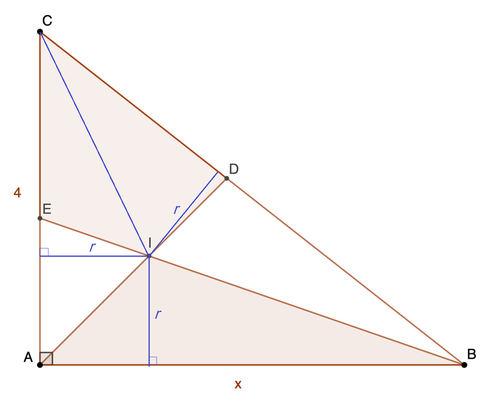
Let B C = y = x 2 + 4 2 and the inradius be r . Then the area of △ A I B , [ A I B ] = 2 r x and that of quadrilateral E I D C :
[ E I D C ] 2 r x ⟹ x ⟹ x = C A C E [ C I A ] + B C C D [ B I C ] = x + y y ⋅ 2 4 r + x + 4 4 ⋅ 2 r y = x + y 2 r y + x + 4 2 r y = x + y 2 r y + x + 4 2 r y = x + y 4 y + x + 4 4 y = x + x 2 + 1 6 4 x 2 + 1 6 + x + 4 4 x 2 + 1 6 = 2 2 + 2 5 ≈ 5 . 0 8 8 0 7 8 5 9 8 By angle bisector theorem, A E C E = A B B C = x y , B D C D = x 4 Since [ E I D C ] = [ A I B ] Solving the equation
Therefore ⌊ 1 0 4 x ⌋ = 5 0 8 8 0 .
Reference: Angle bisector theorem
Claim: A B = C E + C D Proof: Note that the perpendiculars drawn from I to the sides A B , B C and C A all have length r (inradius), since the foot of the perpendiculars (from I ) lie on the incircle
So we can rewrite the given area condition as, [ △ A I B ] 2 A B ⋅ r ⟹ A B = [ △ C I E ] + [ △ C I D ] = 2 C E ⋅ r + 2 C D ⋅ r = C E + C D
Note that the incenter , I lies on the angle bisectors of ∠ A and ∠ B . Using the angle bisector theorem , C E A E = x 2 + 1 6 x ⟹ C E + C E ⋅ x 2 + 1 6 x = 4 ⟹ C E = x + x 2 + 1 6 4 x 2 + 1 6 Similarly, C D B D = 4 x ⟹ C D + C D ⋅ 4 x = x 2 + 1 6 ⟹ C D = x + 4 4 x 2 + 1 6
Using the above claim, A B ⟹ x = C E + C D = x + x 2 + 1 6 4 x 2 + 1 6 + x + 4 4 x 2 + 1 6 Solving the above equation gives x = ± 2 2 + 2 5 ≈ 5 . 0 8 8 0 7 8 5 9 ⟹ ⌊ 1 0 4 ⋅ x ⌋ = 5 0 8 8 0