Pentagonal Diagonal
What is the length of a diagonal of a regular pentagon of unit side length? Give your answer to three decimal places.
Please post your solution!
The answer is 1.618.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
I'm curious: Using roots of unity, for n ⩾ 4 , can we find all the diagonal lengths of any regular n -gon with side length 1?
Log in to reply
The same method can be applied for regular ( 2 n + 1 ) -gons of unit side lengths but it might not necessarily be easier to compute by hand!
Haha I'm sure there are many different approaches available online. What's your solution? Anyway, thanks for solving!
Log in to reply
Use cosine rule, and find the exact form of sin 5 4 ∘ . Pretty rudimentary stuff.
The interior angle of a regular pentagon is 1 8 0 ∘ × ( 1 − 5 2 ) = 1 0 8 ∘ . Hence by cosine rule, the diagonal in question, D satisfies D 2 = 2 ⋅ 1 2 ( 1 − cos 1 0 8 ∘ ) . Using the double angle identity, 1 − cos ( 2 A ) = 2 sin 2 A , we have D 2 = 4 sin 2 5 4 ∘ ⟹ D = 2 sin 5 4 ∘ .
What's left is to find the exact form of sin 5 4 ∘ = cos 3 6 ∘ . Since 3 6 ∘ × 4 = 1 8 0 ∘ − 3 6 ∘ , let B = 3 6 ∘ , we have 4 B = 1 8 0 ∘ − B ⟹ cos ( 4 B ) = cos ( 1 8 0 ∘ − B ) = − cos ( B ) .
Apply the double angle formula repeatedly gives 2 ( 2 cos 2 B − 1 ) 2 − 1 + cos B = 0 . For simplicities sake, let y = cos B . We have 8 y 4 − 8 y 2 + y + 1 = 0 , or ( y + 1 ) ( 2 y − 1 ) ( 4 y 2 − 2 y − 1 ) = 0 .
Since 0 < y = cos 3 6 ∘ > cos 6 0 ∘ = 2 1 , then y = 4 1 + 5 only (via quadratic formula).
Thus, the answer is D = 2 sin 5 4 ∘ = 2 cos 3 6 ∘ = 2 1 + 5 ≈ 1 . 6 1 8 .
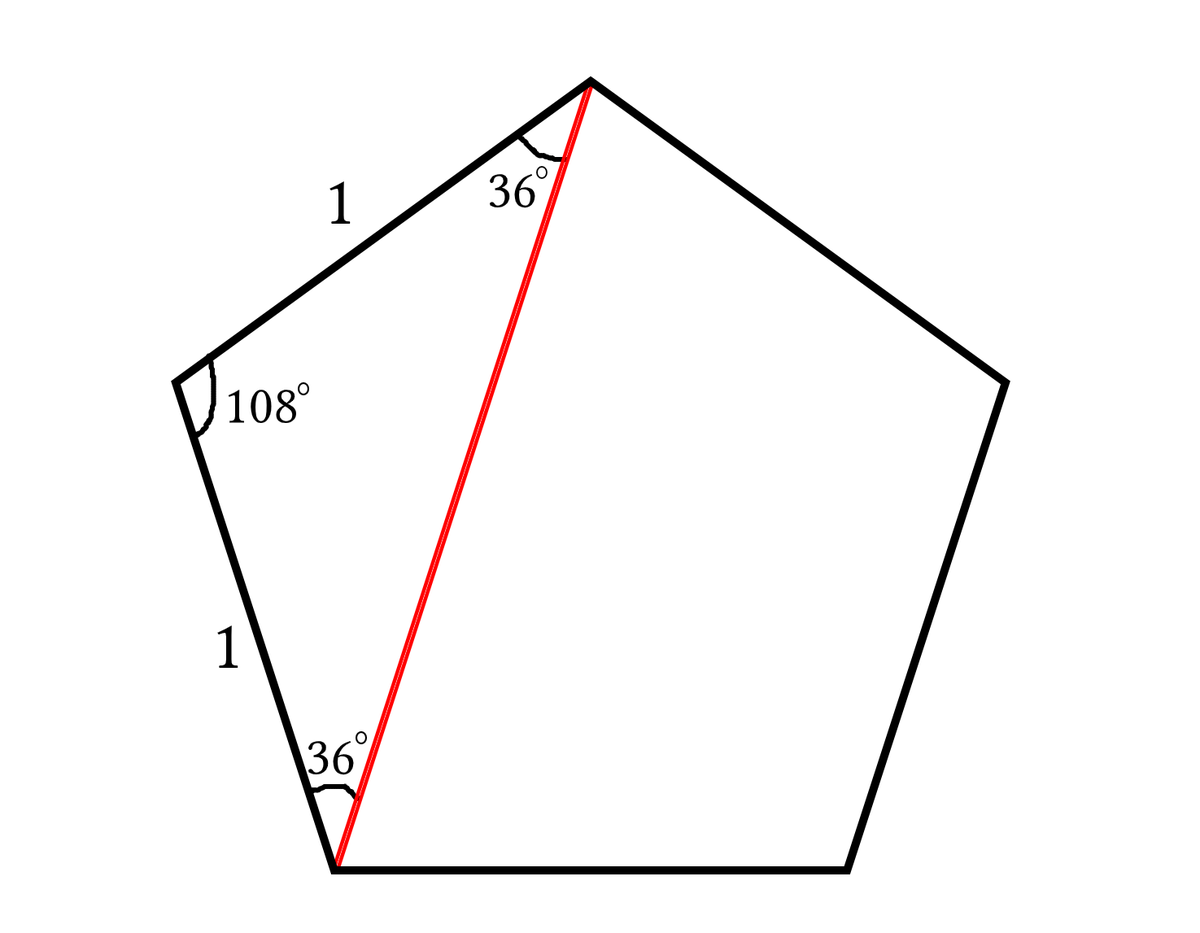 The length of red diagonal is
1
cos
3
6
°
+
1
cos
3
6
°
=
2
cos
3
6
°
=
2
5
+
1
≈
1
.
6
1
8
The length of red diagonal is
1
cos
3
6
°
+
1
cos
3
6
°
=
2
cos
3
6
°
=
2
5
+
1
≈
1
.
6
1
8
But how would you know that cos 3 0 ° = 2 5 + 1 ?
Log in to reply
cos 3 6 ° = 1 − 2 sin 2 1 8 °
Let θ = 1 8 ° . Then 3 θ + 2 θ = 5 θ = 9 0 ° ⇒ 3 θ = 9 0 ° − 2 θ ⇒ sin 3 θ = cos 2 θ ⇒ 3 sin θ − 4 sin 3 θ = 1 − 2 sin 2 θ ⇒ 4 sin 3 θ − 2 sin 2 θ − 3 sin θ + 1 = 0 ⇒ ( sin θ − 1 ) ( 4 sin 2 θ + 2 sin θ − 1 ) = 0
Solving the quadratic equation we get
sin θ = sin 1 8 ° = 4 5 − 1
⇒ sin 2 1 8 ° = 1 6 6 − 2 5 = 8 3 − 5
⇒ 2 sin 2 1 8 ° = 4 3 − 5
⇒ cos 3 6 ° = 1 − 2 sin 2 1 8 ° = 1 − 4 3 − 5 = 4 1 + 5
My solution:
Let ω be the principal fifth root of unity.
ω 5 1 + ω + ω ² + ω ³ + ω 4 ω ² 1 + ω 1 + 1 + ω + ω ² ( u ² − 2 ) + u + 1 u ² + u − 1 ω + ω 1 = u = 1 = 0 = 0 = 0 = 0 = 2 5 − 1 ( ∗ ) ( u = ω + ω 1 ) ( ∗ ∗ )
Also, from ( ∗ ) ,
1 + ω = − ω ² ( 1 + ω + ω ² ) = − ω ³ ( ω + ω 1 + 1 ) = − ω ³ ( 2 5 + 1 ) (using (**) ) .
Length of diagonal is ∣ 1 + ω ∣ = 2 5 + 1 = 1 . 6 1 8
as ∣ ω ³ ∣ = 1 .
The solution also happens to be the golden ratio.