Pentagonal Numbers - Finding The Formula
 Which of the following functions satisfy
f
(
n
+
1
)
−
f
(
n
)
=
3
n
+
1
and
f
(
1
)
=
1
?
Which of the following functions satisfy
f
(
n
+
1
)
−
f
(
n
)
=
3
n
+
1
and
f
(
1
)
=
1
?
Do you understand why this gives us the formula for the n th Pentagonal Number?
This question is part of Calvin's set What Makes A Number Pentagonal?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
12 solutions
Discussions for this problem are now closed
We test the given functions in the options. Firstly, because we want f ( 1 ) = 1 , we only have to consider the options of f ( n ) = 2 n ( n + 1 ) or f ( n ) = 2 ( 3 n − 1 ) n .
Next, we check the other condition. For f ( n ) = 2 n ( n + 1 ) , we have f ( n + 1 ) − f ( n ) = 2 ( n + 1 ) ( n + 2 ) − n ( n + 1 ) = n + 1 , which doesn't satisfy the condition.
For f ( n ) = 2 n ( 3 n − 1 ) , we have f ( n + 1 ) − f ( n ) = 2 ( n + 1 ) ( 3 n + 2 ) − n ( 3 n − 1 ) = 3 n + 1 , hence this is the answer.
I don't like this solution. You are just putting formula into the choices. Not the way to solve a problem. Nitin below got it right.
sir. this formula is first principle method, then the coefficient 2 is use here how and why are u using how, can't understand, let explan.
f ( 1 ) = 1
f ( 2 ) = 1 + 4 = 5
f ( 3 ) = 1 + 4 + 7 = 1 2
. . .
f ( n ) = 1 + 4 + 7 + . . . + ( 3 n − 2 ) = 2 n ( 1 + 3 n − 2 ) = 2 3 n 2 − n
i don't know...i just guess...
yeah. me too. :)
Your solution doesn't answer the question that is posed.
It asks you to find f ( n ) such that f ( n + 1 ) − f ( n ) = 3 n + 1 .
f(2)-f(1)=3 2+1, similarly it can be written till f(n)-f(n-1)=3 n+1, adding all these functions , by telescopic summation what we get is f(n)-f(1)=3(n+(n-1)+n(-2).......+2)+n*1; computing the value of f(n) from here will result in f(n)=n(3n-1)/2;
U s e t h e m e t h o d o f f i n i t e d i f f e r e n c e s t o f i n d t h e p o l y n o m i a l f o r a n y i n t e g e r s e q u e n c e s t h a t c a n b e e x p r e s s e d b y a p o l y n o m i a l . 1 , 5 , 1 2 , 2 2 , 3 5 4 , 7 , 1 0 , 1 2 3 , 3 , 3 0 , 0 L e t a 0 = 1 , a 1 = 4 , a 2 = 3 , a 3 = 0 , . . . , t h e f i r s t i n t e g e r i n s u c c e s s i v e r o w s . T h e n t h e p o l y n o m i a l t h a t w i l l g i v e t h e n t h t e r m i s : a 0 0 ! ( n − 1 − 0 ) ! ( n − 1 ) ! + a 1 1 ! ( n − 1 − 1 ) ! ( n − 1 ) ! + a 2 2 ! ( n − 1 − 2 ) ! ( n − 1 ) ! + a 3 3 ! ( n − 1 − 3 ) ! ( n − 1 ) ! + . . . w h i c h s i m p l i f i e s t o 2 1 n ( 3 n − 1 ) f o r t h i s i n t e g e r s e q u e n c e g i v e n .
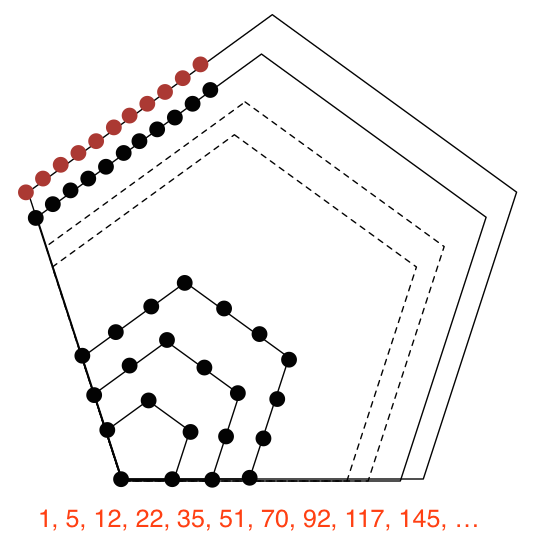
the pentagonal nos.are as follows:
1
1+4=5
1+4+7=12
1+4+7+10=22
1+4+7+10+13=35
.....
this is an AP series with d=3
sum of A.P series =(n/2){2a+(n-1)d)
putting d=3 and a=1,
we get (n/2)(3n-1) which is the required ans.
ONLY f(n)=(3n-1)n/2 satisfy the two requirements like f(1)=1 and f(n+1)-f(n)=4
The solution is how we can examine that answer by match into the right answer
by putting simple values
we get d as answer
for, f(n+1)-f(n)=(n+1)(n+2)-n(n+1)/2=n+1 for n>1,which contradicts,where f(n)=n(n+1)/2 for f(n)=(3n-1)n/2, f(n+1)-f(n)=3n+1,hence the result
By putting the values 1,2,3... if gives the result of the sequence means that formula is correct. as f(n)=(3n-1)(n)/2
just see the pattern is 1,5 , 12 , 22 , 35 , 51 ... => 4, 7 , 10 , 13 , 16 , 19 ... incise 3 in every time.. then we make a equation like (3n^2-1) / 2
If we know f(3)=12, you just try the options. But that's not beautifil, I admit.
f ( n + 1 ) − f ( n ) = 3 n + 1
Put n+1=N
f ( N ) − f ( N − 1 ) = 3 N − 2
f ( N − 1 ) − f ( N − 2 ) = 3 ( N − 1 ) − 2
.
.
.
f ( 2 ) − f ( 1 ) = 3 × 2 − 2
Take the sum of all equations
f ( N ) − f ( N − 1 ) + f ( N − 1 ) − f ( N − 2 ) + . . . . . . − f ( 2 ) + f ( 2 ) − f ( 1 ) = 3 ∑ i = 2 N N − 2 ( N − 1 )
f ( N ) − 1 = 3 ( 2 N ( N + 1 ) − 1 ) − 2 N + 2
f ( N ) = [ 3 ( N 2 + N − 2 ) − 4 N + 6 ] / 2
= 2 3 N 2 + 3 N − 4 N
= 2 3 N 2 − N
= 2 N ( 3 N − 1 )
Change of variables:
f ( n ) = 2 ( 3 n − 1 ) ( n )