Place Your Tip in the Envelope
Let be a point inside circle with center at and a radius , and let . For every point on circle , a perpendicular straight line is drawn through the midpoint of .
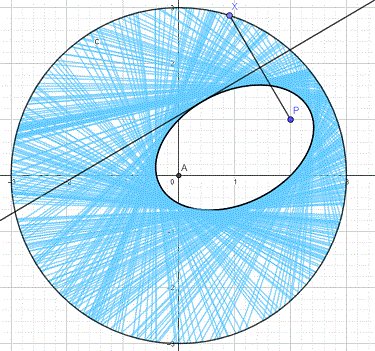
If the area inside the envelope of the family of all these straight lines is of the area of circle , then the ratio is , where and are co-prime integers. Find .
The answer is 9.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Without loss of generality because of rotational symmetry, let P be on the x -axis with coordinates ( p , 0 ) .
Since X is on the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 = r 2 , let its coordinates be ( k , r 2 − k 2 ) .
Then the midpoint of X P is ( 2 p + k , 2 r 2 − k 2 ) , the slope of X P is k − p r 2 − p 2 , and the perpendicular bisector of X P is y = − r 2 − k 2 p − k ( x − 2 p + k ) + 2 r 2 − k 2 or y = 2 r 2 − k 2 2 p x − 2 k x − p 2 + r 2 .
The top part of the ellipse follows the minimum height of each x -value over all k -values, which occurs when d k d y = 0 . Therefore, d k d y = 4 ( r 2 − k 2 ) 3 2 k p x − k p 2 + k r 2 − 2 r 2 x = 0 , which solves to k = 2 p x − p 2 + r 2 2 r 2 x .
Substituting k = 2 p x − p 2 + r 2 2 r 2 x into y = 2 r 2 − k 2 2 p x − 2 k x − p 2 + r 2 and simplifying gives y 2 = 4 r 2 ( r − 2 x + p ) ( r + 2 x − p ) ( r − p ) ( r + p ) , which can further be simplified to ( 2 r ) 2 ( x − 2 p ) 2 + ( 2 r ) 2 − ( 2 p ) 2 y 2 = 1 , an equation of an ellipse in standard form with a major axis of a = 2 r and a minor axis of b = ( 2 r ) 2 − ( 2 p ) 2 = 2 1 r 1 − ( r p ) 2 .
The ratio of the area of the ellipse to the area of the circle is then π r 2 π a b = π r 2 π ⋅ 2 r ⋅ 2 1 r 1 − ( r p ) 2 = 4 1 1 − ( r p ) 2 . Setting this equal to the ratio of areas of 1 5 % gives 4 1 1 − ( r p ) 2 = 1 0 0 1 5 , which solves to r p = 5 4 . Therefore, m = 4 , n = 5 , and m + n = 9 .