An algebra problem by prashant goyal
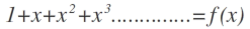 then what is the value of f(x) at x=1/2?
then what is the value of f(x) at x=1/2?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
the terms are in gp with r=x=1/2. the sum to infinity in a gp where -1<r<1=a/(1-r). substituting a=1, r=1/2, we get 2 as the answer. Nice sum.
Clearly f ( x ) is a GP with ratio x (if ∣ x ∣ < 1 ) then: f ( x ) = 1 − x 1 f ( 2 1 ) = 1 − 2 1 1 f ( 2 1 ) = 2
Did the same
f ( x ) = 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + . . . = n = 0 ∑ ∞ x n So f ( x ) is a geometric progression and its value is given by: n = 0 ∑ ∞ x n = 1 − x 1 Since x = 2 1 , therefore: f ( 2 1 ) = 1 − 2 1 1 = 2
Just use the sum of infinite geometric sequence formula for the x's. Then add 1 to the result.
G i v e n t h a t 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . = f ( x ) . . . . . . . . . . . . ( i ) P u t t i n g x = 2 1 i n ( i ) ∵ x = 2 1 w e h a v e f ( x ) = 1 + 2 1 + 4 1 + 8 1 + . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . M u l t i p l y i n g b o t h s i d e s b y " 2 " w e g e t 2 f ( x ) = 2 + 2 1 + 4 1 + 8 1 + . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . o r 2 f ( x ) = 2 + f ( x ) ∵ f ( x ) = 1 + 2 1 + 4 1 + 8 1 + . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . o r 2 f ( x ) − f ( x ) = 2 o r f ( x ) = 2