Playing with Triangles!
In a Δ A B C , let A B = A C = 5 , B C = 6 . Let E be a point on A C and F be a point on A B such that B E = C F , ∠ E B C = ∠ F C B and sin ( θ ) = 1 3 5 , where θ = ∠ E B C . Let H be the point of intersection of B E and C F , and let K be a point on B C such that H K is perpendicular to B C .
If the length of H K can be represented as β α where α , β ∈ Z + , g cd ( α , β ) = 1 , submit the value of α + β as your answer.
The answer is 1941.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Let B E = C F = a and ∠ A B C = ∠ A C B = ϕ = sin − 1 ( 5 4 ) . Using Sine Rule in △ E B C , we have:
sin ϕ a ⇒ a = sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − θ − ϕ ) 6 = sin ( θ + ϕ ) 6 = sin ( θ + ϕ ) 6 sin ϕ = sin θ cos ϕ + sin ϕ cos θ 6 sin ϕ = 1 3 5 × 5 3 + 5 4 × 1 3 1 2 6 × 5 4 = 2 1 1 0 4
Let ∠ B F C = γ . Using Sine Rule in △ F B C , we have:
6 sin γ ⇒ sin γ = a sin ϕ = 6 × 5 4 × 1 0 4 2 1 = 6 5 6 3 ⇒ cos γ = 6 5 1 6
Then ∠ F C B = δ = 1 8 0 ∘ − ϕ − γ .
⇒ sin δ ⇒ tan δ = sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − ϕ − γ ) = sin ( ϕ + γ ) = 5 4 × 6 5 1 6 + 6 5 6 3 × 5 3 = 3 2 5 2 5 3 = 2 0 4 2 5 3
Now, let B K = x . therefore, K C = 6 − x and H K = y . Then, we have:
y ⇒ 1 2 5 x x ⇒ y α + β = x tan θ = ( 6 − x ) tan δ = 2 0 4 2 5 3 ( 6 − x ) = 1 6 9 7 5 9 = x tan θ = 1 6 9 7 5 9 × 1 2 5 = 6 7 6 1 2 6 5 = 1 2 6 5 + 6 7 6 = 1 9 4 1
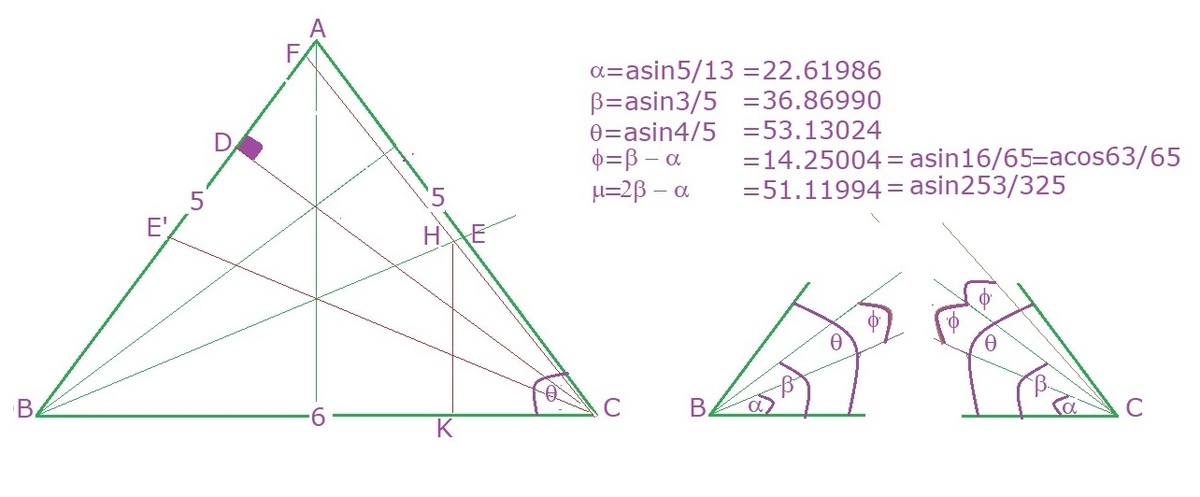
Notice that ∠ B = ∠ C , so let ∠ B = ∠ C = β .
First we find sin β and cos β , this is easy since this is an isosceles triangle:
sin β = 5 4 and cos β = 5 3 .
Also, we find that cos θ = 1 3 1 2 , sin ( 2 β ) = 2 5 2 4 and cos ( 2 β ) = − 2 5 7 . We are going to use these values later.
Then let ∠ B C F = α , so ∠ B F C = 1 8 0 ∘ − α − β and ∠ B E C = 1 8 0 − β − θ . Now apply sine rule on △ B F C :
sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − α − β ) 6 = sin β C F
And in △ B E C :
sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − θ − β ) 6 = sin β B E
Since B E = C F :
sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − α − β ) 6 = sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − θ − β ) 6 sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − ( α + β ) ) = sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − ( θ + β ) ) sin ( α + β ) = sin ( θ + β )
But since α = θ , then α = 1 8 0 ∘ − ( θ + 2 β ) .
Now, ∠ B H C = 1 8 0 ∘ − θ − α = 2 β .
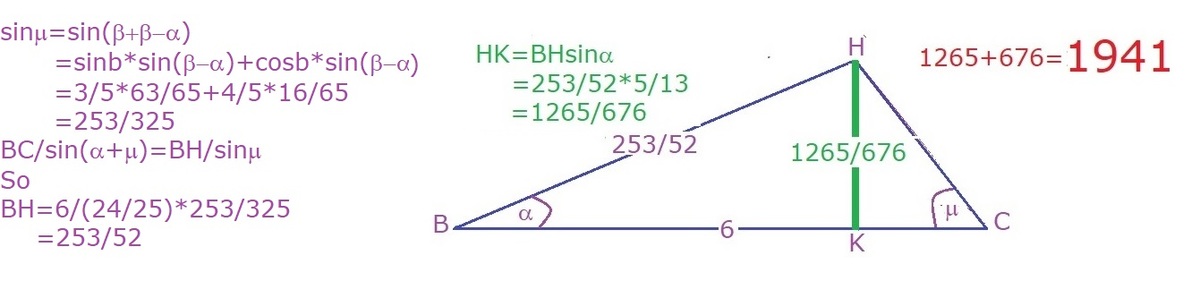
Then, calculate B H using sine rule again:
sin α B H = sin ∠ B H C 6 B H = sin ( 2 β ) 6 sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − ( θ + 2 β ) ) = sin ( 2 β ) 6 sin ( θ + 2 β )
Finally,
sin θ = B H H K ⟹ H K = B H sin θ H K = sin ( 2 β ) 6 sin ( θ + 2 β ) sin θ H K = sin ( 2 β ) 6 ( sin θ cos ( 2 β ) + cos θ sin ( 2 β ) ) sin θ H K = 2 5 2 4 6 ( 1 3 5 ⋅ 2 5 − 7 + 1 3 1 2 ⋅ 2 5 2 4 ) ( 1 3 5 ) H K = 6 7 6 1 2 6 5 .
Thus, the final answer is 1 2 6 5 + 6 7 6 = 1 9 4 1 .