Please Excuse My Dear Ant Brilli
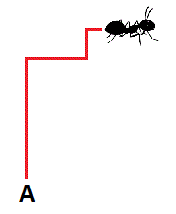 If Brilli the Ant starts at point
A
and crawls up
1
p
1
units, then right
2
p
1
units, then up
3
p
1
units, then right
4
p
1
units, and continues to crawl in this pattern indefinitely, he will get closer and closer to point
B
.
If Brilli the Ant starts at point
A
and crawls up
1
p
1
units, then right
2
p
1
units, then up
3
p
1
units, then right
4
p
1
units, and continues to crawl in this pattern indefinitely, he will get closer and closer to point
B
.
If p is an integer and the slope of A B is 1 6 1 of a perfect number , find p .
The answer is 5.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Assume an unorthodox notation, where
n
′
=
n
p
1
, e.g.
2
′
=
2
p
1
.
Let
EV
=
n
=
0
∑
∞
(
2
n
)
p
1
=
2
′
+
4
′
+
6
′
+
8
′
+
⋯
and
OD
=
n
=
0
∑
∞
(
2
n
−
1
)
p
1
=
1
′
+
3
′
+
5
′
+
7
′
+
⋯
.
Note that
OD EV ( 1 − 2 ′ ) OD EV Slope of A B = 1 ′ + 3 ′ + 5 ′ + 7 + ⋯ 2 ′ + 4 ′ + 6 ′ + 8 ′ + … = 1 ′ + 3 ′ + 5 ′ + 7 + ⋯ 2 ′ ( 1 ′ + 2 ′ + 3 ′ + 4 ′ + … ) = OD 2 ′ [ OD + EV ] = 2 ′ ( 1 + OD EV ) = 2 ′ = EV OD = 2 ′ 1 − 2 ′ = 2 ′ 1 − 1 = 2 p − 1
It is given that
Slope of
A
B
∴
2
p
−
1
=
1
6
1
N
=
1
6
1
⋅
2
q
−
1
(
2
q
−
1
)
N
(
N
=
perfect number
)
(
q
prime
)
Therefore, 2 q − 1 = 1 6 and p = q i.e. p ( = q ) = 5
The ant goes up Δ y = n = 1 ∑ ∞ ( 2 n − 1 ) p 1 and right Δ x = n = 1 ∑ ∞ ( 2 n ) p 1 .
Let k = n = 1 ∑ ∞ n p 1 . Then Δ x = n = 1 ∑ ∞ ( 2 n ) p 1 = 2 p 1 n = 1 ∑ ∞ n p 1 = 2 p 1 k , and Δ y = k − Δ x = k − 2 p 1 k = 2 p 2 p − 1 k .
The slope of A B is therefore m = Δ x Δ y = 2 p 1 k 2 p 2 p − 1 k = 2 p − 1 .
Since the slope m is equal to 1 6 1 of a perfect number P , then P = 1 6 m = 1 6 ( 2 p − 1 ) .
Since all even perfect numbers are in the form of 2 p − 1 ( 2 p − 1 ) and 1 6 is its only even factor, 1 6 = 2 p − 1 , and this solves to p = 5 .
Slope of the line segment A B is 2 p 1 + 4 p 1 + 6 p 1 + . . . 1 p 1 + 3 p 1 + 5 p 1 + . . . = 2 p − 1 = 1 6 1 × 4 9 6 . 4 9 6 is a perfect number. So 2 p − 1 = 3 1 or 2 p = 3 2 = 2 5 . Hence p = 5 .
(If p and 2 p − 1 be primes, then 2 p − 1 ( 2 p − 1 ) is a perfect number. So, for prime p , 2 p − 1 is ( 2 p − 1 1 ) t h of a perfect number. Hence 2 p − 1 = 1 6 = 2 4 , and from here, p = 5 , a prime number.)