Potential on a cone
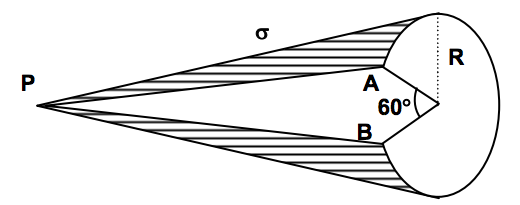
A non-conducting hollow cone has charge density . A part is cut and removed from the cone. The potential due to the remaining portion of the cone at point is
,
where are natural numbers.
Find .
The answer is 17.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
All six 60 degree slices contribute equally. So calculate the potential due to the entire (full) cone, and then multiply that by 6 5 . The key to this problem is knowing what the area element is. It can be derived using standard multi-variate calculus as indicated here . Suppose the cone has height H and radius R , and that its length is along the z -direction.
d S = 1 + R 2 H 2 r d r d θ
The differential charge is thus:
d Q = σ d S = σ 1 + R 2 H 2 r d r d θ
The relationship between the vertical position and the radial position is:
z = H − R H r
The distance between an area element and the top of the cone is:
D = r 2 + ( H − z ) 2 = r 2 + R 2 H 2 r 2 = 1 + R 2 H 2 r
The differential electric potential contribution is:
d U = 4 π ϵ 0 D d Q = 4 π ϵ 0 1 + R 2 H 2 r σ 1 + R 2 H 2 r d r d θ = 4 π ϵ 0 σ d r d θ
The total electric potential for the full cone is:
U = ∫ 0 2 π ∫ 0 R 4 π ϵ 0 σ d r d θ = 2 ϵ 0 σ R
The electric potential for the reduced cone is:
U r = 6 5 U = 1 2 ϵ 0 5 σ R