Problem 9
The number of real solutions of the equation 1 + cos 2 x = 2 sin − 1 ( sin x ) where − π ≤ x ≤ π .
The answer is 2.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Nice solution , upvoted
It was quite amazing that number of solutions are in decimals . :)
Agree with you. That makes me laugh.
Sir generally people try it by hit and trial method.So I set it to decimal
Log in to reply
In that case, you could increase the domain of x to greater values for example x ∈ [ − 5 π , 5 π ] .
1 + cos ( 2 x ) = 2 ⋅ sin − 1 ( sin x ) sin − 1 ( sin x ) = 2 1 + cos ( 2 x ) sin − 1 ( sin x ) = 2 1 + cos ( 2 x ) sin − 1 ( sin x ) = cos 2 x sin − 1 ( sin x ) = ± cos x sin ( ± cos x ) = sin x ⇒ { sin ( − c o s x ) = sin x sin ( c o s x ) = sin x
Igualando-as,
{ sin ( − c o s x ) = sin x sin ( c o s x ) = sin x ⇒ { − c o s x = x c o s x = x
Igualando-as, novamente:
x = x − cos x = cos x 2 ⋅ cos x = 0 cos x = 0
Logo, temos que S = { − 2 π , 2 π }
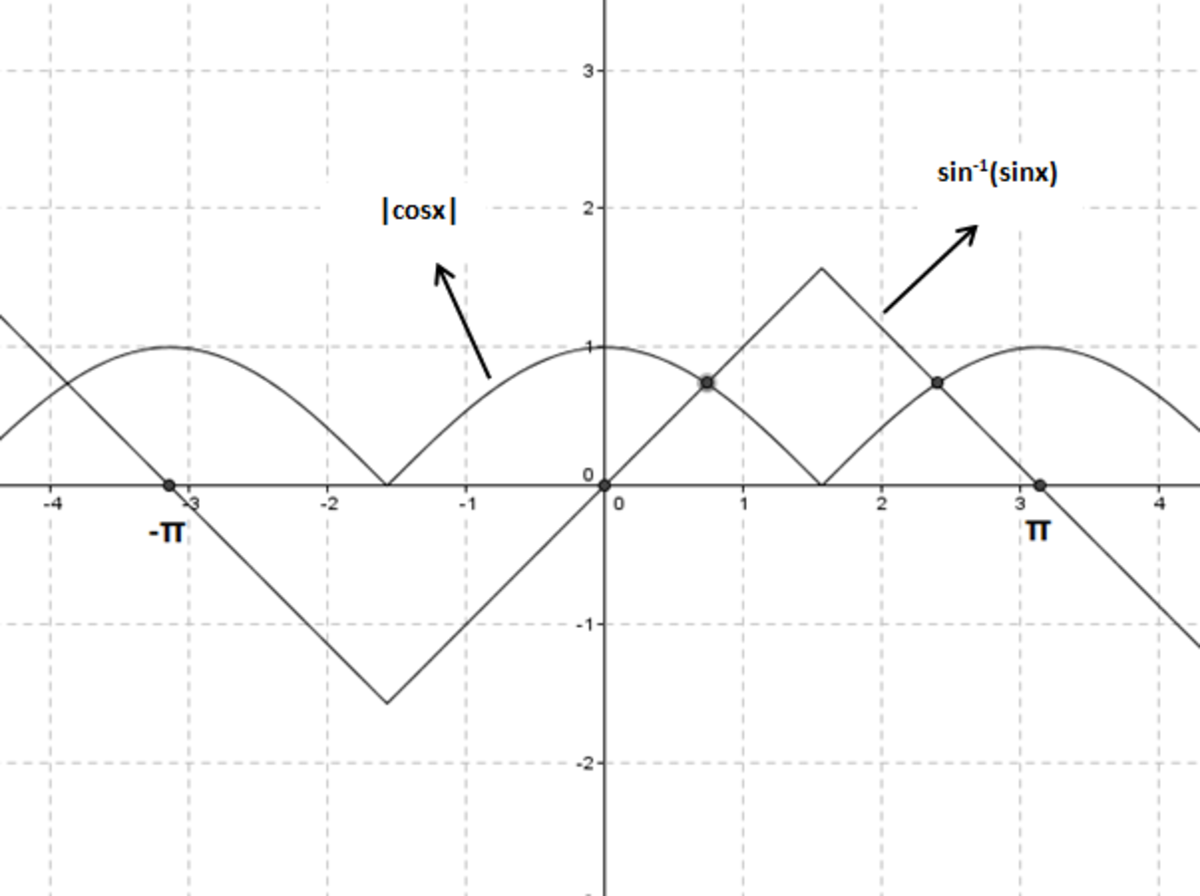
1 + cos 2 x = 2 sin − 1 ( sin x )
⟹ 2 ∣ c o s x ∣ = 2 s i n − 1 ( s i n x )
⟹ ∣ c o s x ∣ = s i n − 1 ( s i n x ) .
When we draw the graph both functions (shown below) we can actually see that they intersect only at two points ∀ x ∈ − π ≤ x ≤ π .