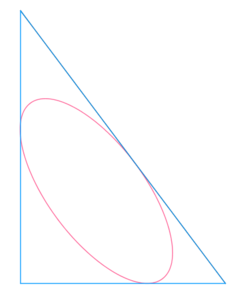
Projected Incircle
 A plane
a
has an equation:
3
x
+
4
y
+
5
z
=
1
A triangle has as its vertices points of intersection of the plane
a
with the axes of the coordinate system. Incircle of that triangle is projected onto the
X
Y
plane and the projected shape has an area
A
.
Give answer as
⌊
A
×
1
0
0
0
0
⌋
A plane
a
has an equation:
3
x
+
4
y
+
5
z
=
1
A triangle has as its vertices points of intersection of the plane
a
with the axes of the coordinate system. Incircle of that triangle is projected onto the
X
Y
plane and the projected shape has an area
A
.
Give answer as
⌊
A
×
1
0
0
0
0
⌋
The answer is 35198.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
S c i r c l e cos θ = S e l l i p s e , where θ - is angle between plane a and plane z = 0 and cos θ = 3 2 1 + 4 2 1 + 5 2 1 5 1
Vertices of the triangle are A ( 3 , 0 , 0 ) , B ( 0 , 4 , 0 ) and C ( 0 , 0 , 5 ) . Sides can be easily calculated using Pythagorean theorem: 5 , 3 4 , 4 1 . The radius of the incircle can be calculated using the formula: r = s △ A B C where s is a semi-perimeter. Area of △ A B C can be found using De Gua's theorem: ( △ A B C ) 2 = ( ( 3 × 4 ) 2 + ( 3 × 5 ) 2 + ( 4 × 5 ) 2 ) / 4 ⇒ △ A B C = 2 7 6 9 The projected incircle is ellipses with major axis = 2 r . Minor axis can be obtained by multiplying length of major axis with "the shortening factor". That shortening factor is 1 − flattening factor of the the ellipse g . It is really cosine of the angle between plane XY and plane a. It is also a ratio of original segment lengths to the projected ones, perpendicular to the intersection line between the two planes.
The shortening factor is of the △ A B C can be obtained as △ A B C △ A B O = 7 6 9 3 × 4 where O is the point of origin. The area of the ellipse will be: π r 2 7 6 9 1 2 = 6 7 6 9 π / ( 3 4 4 1 + 5 3 4 + 5 4 1 + 5 0 )