Proton Beam Hitting Its Target
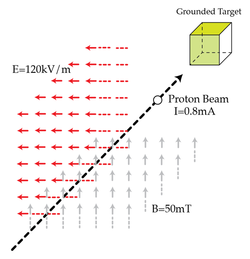 A non-relativistic proton beam passes without deflection through a region where there are two transverse, mutually perpendicular, electric (
) and magnetic (
) fields. Then the beam strikes a grounded target. Find the force
in Newtons
with which the beam acts on the target if the beam current is
.
A non-relativistic proton beam passes without deflection through a region where there are two transverse, mutually perpendicular, electric (
) and magnetic (
) fields. Then the beam strikes a grounded target. Find the force
in Newtons
with which the beam acts on the target if the beam current is
.
Assume that the collisions with the target are inelastic.
The proton's mass and charge are:
The answer is 0.00002.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
If there is no deflection, then the two opposing forces must cancel each other.
In other words,
Electric force = Magnetic force
Hence,
q E = B v q ,
where q is the charge of a single particle, and v is the velocity of that particle.
⇒ v = B E
Now,
i = d t d q = η × e ,
where η is the no. of particles crossing a point per unit time, and e is the charge of a proton
⇒ η = e i
Finally, we find the force exerted on the target.
F = η d t d p = η × ( p f i n a l − p i n i t i a l ) = − η × p i n i t i a l = − η × m p v
∣ F ∣ = η × m p v
Substituting the values of η and v , we get,
∣ F ∣ = e i B E m p ≈ 2 × 1 0 − 5 N