Pyramids and Circles!
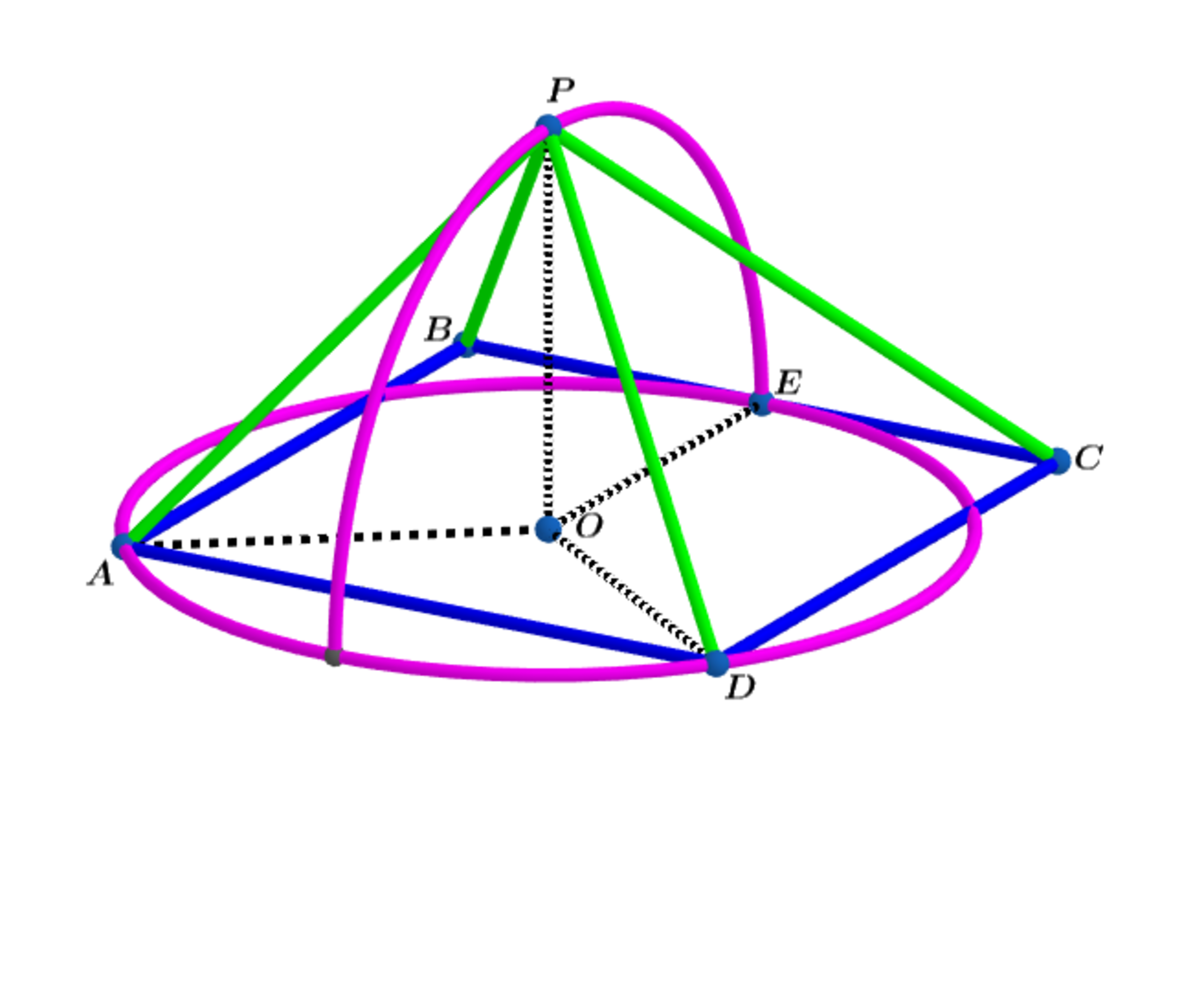
In , the circle with center passes through vertices and and is tangent to at .
Folding the arc of the semi-circle at a right angle, as shown above, the radius of the semicircle becomes the height of the pyramid.
Let be the lateral surface area of the pyramid above.
If , where and are coprime positive integers, find
.
The answer is 86.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let 2 z be the length of a side of square base A B C D and let A : ( 0 , 0 ) , B : ( 0 , 2 z ) ,
C : ( 2 z , 2 z ) , D : ( 2 z , 0 ) and E : ( z , 2 z ) and O : ( x , y ) .
( 1 ) : ( x − z ) 2 + ( y − 2 z ) 2 = r 2
( 2 ) : x 2 + y 2 = r 2
( 3 ) : ( x − 2 z ) 2 + y 2 = r 2
Subtracting ( 2 ) from ( 1 ) ⟹ 2 z x + 4 z y = 5 z 2
and
Subtracting ( 2 ) from ( 3 ) ⟹ 4 z ( z − x ) = 0 and z = 0 ⟹ x = z ⟹
y = 4 3 z ⟹ r = 4 5 z
For triangular face A P D the slant height s 1 = ( 4 5 z ) 2 + ( 4 3 z ) 2 = 4 3 4 z
For triangular face B P C the slant height s 2 = ( 4 5 z ) 2 + ( 4 5 z ) 2 = 4 5 2 z
For triangular faces A P B and D P C the slant heights s 3 = s 4 = ( 4 5 z ) 2 + z 2 = 4 4 1 z
⟹ The lateral surface area A = 4 3 4 + 5 2 + 2 4 1 z 2
⟹ A □ A B C D A = 4 3 4 + 5 2 + 2 4 1 =
e a + b c + c d ⟹ a + b + c + d + e = 8 6 .