Pythagoras is Always Right
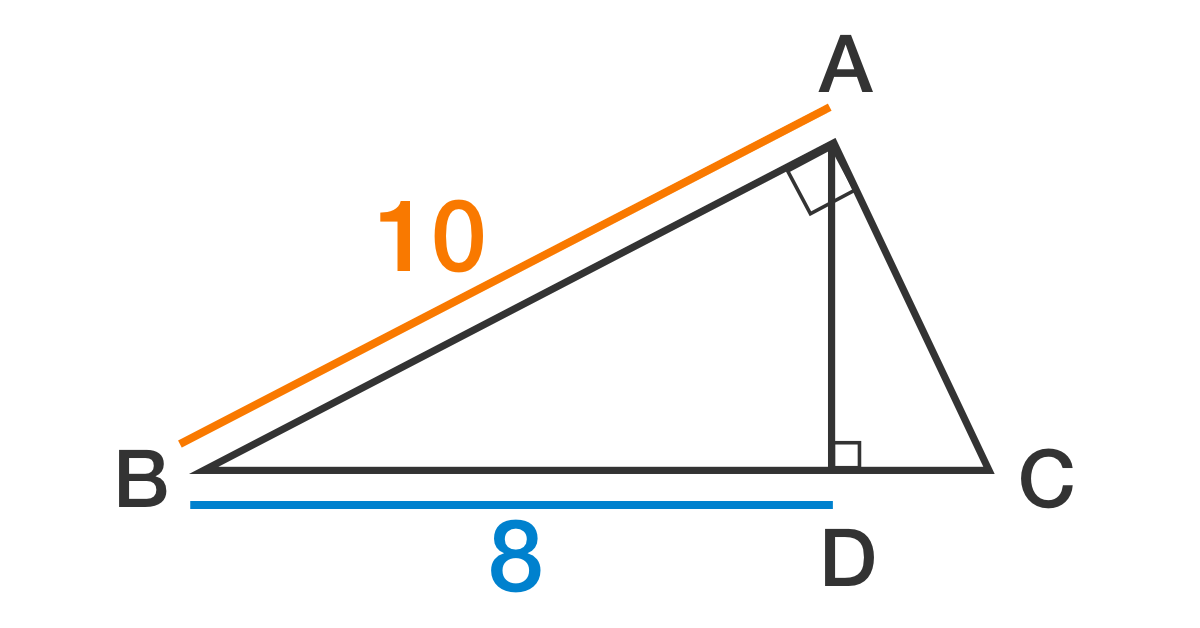
△
A
B
C
is a right triangle and line segment
A
D
is an altitude.
If
A
B
=
1
0
and
B
D
=
8
, then what is the area of
△
A
B
C
?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
9 solutions
That's doing it the hard way.
Once you find the altitude AD is 6, the larger triangle area ABD is 24. Since triangle ABC is larger, eliminate choices that are absurd (75, 85). Now test right triangle ratios for the smallest triangle. A 3-4-5 on a 6 ratio is 4.5-6-7.5. Plug in the hypotenuse and you get the area of 75/2.
Log in to reply
Even easier: the ratio of triangle ABD to triangle ACD is 6/8 or 3/4. That means triangle ACD's base =3/4 of triangle ABD's base and the same goes for the height. So triangle ACD's area is 3/4* 3/4=9/16 of that of triangle ABD. The total area of both triangles then is (1+9/16)* 24=(25/16)*24=75/2.
I got it, thanks
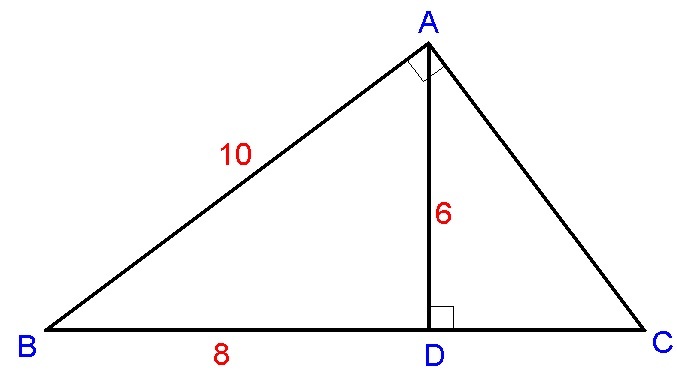 From the properties of a
3
−
4
−
5
right triangle,
A
D
=
6
.
From the properties of a
3
−
4
−
5
right triangle,
A
D
=
6
.
Apply pythagorean theorem at △ A D C .
D C = ( A C ) 2 − 3 6
Since △ A B C ∼ △ A D C , then A D 1 0 = A C B C ⟹ 6 1 0 = A C 8 + D C ⟹ 3 5 = A C 8 + D C
⟹ 5 A C = 2 4 + 3 D C ⟹ 5 A C = 2 4 + 3 ( A C ) 2 − 3 6 ⟹ 5 A C − 2 4 = 3 ( A C ) 2 − 3 6
Squaring both sides, we obtain
( 5 A C − 2 4 ) 2 = ( 3 A C 2 − 3 6 ) 2 ⟹ 1 6 A C 2 − 2 4 0 A C + 9 0 0 = 0
Using the quadratic formula to solve for A C , we get
A C = 7 . 5
Finally, the area of △ A B C is
A = 2 1 ( 1 0 ) ( 7 . 5 ) = 2 7 5
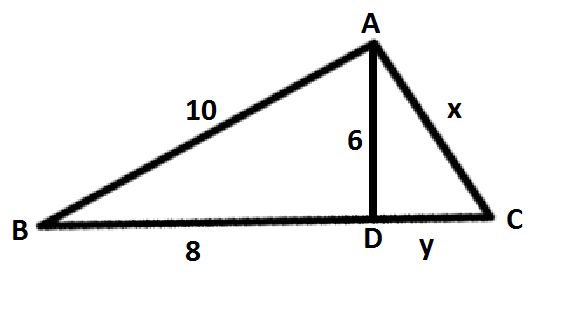
I've done it in the following way,
-
In right triangle ABD by Pythagorean theorum, AD=6 units.
-
Let AC be x and DC be y,
Then in right triangle ABC, by Pythagorean theorum
(8+y)^2=10^2 + x^2
simplifying you'll get x^2= -36 + 16y + y^2----------(1)
-
Next in right triangle ADC,by Pythagorean theorum
x^2= 6^2 + y^2= 36 + y^2-------------------------------(2)
-
Equating (1) and (2) 72=16y
Therefore y= 2 9
- Now substitute this in equation (2),
x^2=36+[ 2 9 ]^2
x^2= 4 2 2 5
So x= 2 1 5
- Now find the area by 2 1 bh
Area(ABC)= 2 1 * 10 * 2 1 5 = 4 1 5 0 = 2 7 5
Therefore answer is 2 7 5 units
Noticed that △ A B D and △ A B C are similar triangles.
Therefore, we have
A D A C = B D A B = A B B C
Note that A r e a = 2 A C × A B
So we need to find the value of A C
We can use A D A C = B D A B , substitute A B = 1 0 , A D = 6 , and B D = 8 , then solve for A C you'll get, A C = 2 1 5
A r e a = 2 A C × A B = 4 1 5 × 1 0 = 2 7 5
AD=√(100-64)=√36=6 so the ratio of triangle ABD to triangle ACD is 6/8 or 3/4. That means triangle ACD's base =3/4 of triangle ABD's base and the same goes for the height. So triangle ACD's area is 3/4* 3/4=9/16 of that of triangle ABD. The total area of both triangles then is (1+9/16)* 24=(25/16)*24=75/2.
∆ABD and ∆ABC are similar,
So, BC/AB = AB/BD,
BC = 10×10/8 = 12.5,
And AD = 6 by Pythagoras theorem.
So area = (1/2)×AD×BC = (1/2)×6×12.5,
= 37.5
AD^2=10^2-8^2=36 so AD=6. Cos(ABC))=sin(ACB) ∆ABC is right angle. Sin(ACB)=0.8 so AC=6÷0.8=7.5 so area of ∆ABC=0.5×10×7.5×sin90=75÷2#######
By pythagoras theorem, AD=6:Triangle BDA Similar Triangle ADC. So BD / AD = AD / DC; 8/6=6/DC. ; DC=(6x6)/8 = 36/8 = 9/2; Ar(ABC) = Ar(ABD) + Ar(ADC) = (1/2 x 8 x 6) + (1/2 x 9/2 x 6) = 24 + 27/2 = 75/2
Using Euclid's theroem in right triangles you can calculate the hypotenuse with the formula AB^2=BC BD to get the result 12.5. The next step is to use Pythagoras theorem to calculate the side AC, which is 7.5. To calculate the area you then need to use the formula AB AC/2 and get the result 75/2
When the original right triangle is cut into two smaller right triangles, both of the small triangles are similar to the original because they each share two angles with the original triangle. Therefore, they are similar with each other and we can set up the ratio A B B D = A C A D .
We also know that because △ A B D is right, A D = 6 . (This can be computed using the Pythagorean Theorem, or recognized because △ A B D is similar to a 3-4-5 right triangle.)
Therefore, A B B D = A C A D → 1 0 8 = x 6 → x = 7 . 5
Therefore, the area of the triangle is 2 base × height = 2 1 ( 1 0 ) ( 7 . 5 ) = 2 7 5 .