Pythagoras theorem
 In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem—or Pythagoras' theorem—is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle.
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem—or Pythagoras' theorem—is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle.
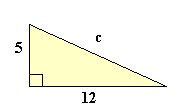
Solve this triangle and comment your solution below.
The answer is 13.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
In pythagoras theorem , [hypetunuse]^2=[base]^2+[side]^2 THEREFORE, c^2=25+144 which is equal to 13
The Pythagorean theorem states that: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 When a = H e i g h t , b = P e r p e n d i c u l a r a n d c = H y p o t e n u s e Setting a = 5 a n d b = 1 2 and solving ,we get: 5 2 + 1 2 2 = c 2 2 5 + 1 4 4 = c 2 1 6 9 = c 2 c = 1 3 Remenber ,we cannot take the negative square root because a triangle(or any figure for that matter)cannot have negative sides.
Pythagorean triplets...
12^2 + 5^2 = c^2 [ pythagoras theorem : base^2 + height^2 = hypotenuse^2] So, c^2 = 169 or , c = 13..
The Pythagoras Theorem states that a 2 + b 2 = c 2 where a and b are the shorter sides and c is the hypotenuse. If we input the given information in the diagram, we get an equation 5 2 + 1 2 2 = c 2 . By solving this, we get 1 6 9 = c 2 , and c = 1 3 .