Quantum Computing 2.2 -- What is my quantum gate?
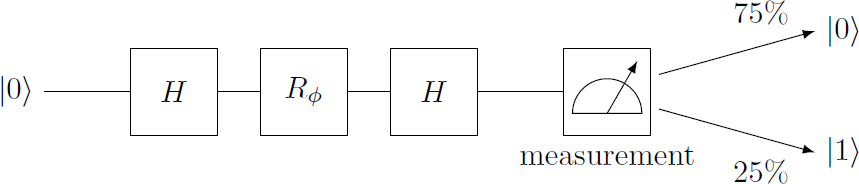
A qubit in the initial state is sent sequentially through the quantum gates , and . The measurement at the end delivers the state in 75% of the cases and the state in 25% of the cases.
What is on possible value for the phase angle ?
Details: The gates and are described in the basis by the matrices where .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Matrix multiplication yields H ⋅ R ϕ ⋅ H = 2 1 ( 1 1 1 − 1 ) ⋅ ( 1 0 0 e i ϕ ) ⋅ ( 1 1 1 − 1 ) = 2 1 ( 1 1 1 − 1 ) ⋅ ( 1 e i ϕ 1 − e i ϕ ) = 2 1 ( 1 + e i ϕ 1 − e − i ϕ 1 − e − i ϕ 1 + e i ϕ ) = 2 e i ϕ / 2 ( e − i ϕ / 2 + e i ϕ / 2 e − i ϕ / 2 − e i ϕ / 2 e − i ϕ / 2 − e i ϕ / 2 e − i ϕ / 2 + e i ϕ / 2 ) = e i ϕ / 2 ( cos 2 ϕ − i sin 2 ϕ − i sin 2 ϕ cos 2 ϕ ) Therefore, the final state is H ⋅ R ϕ ⋅ H ∣ 0 ⟩ = e i ϕ / 2 ⋅ ( cos 2 ϕ ∣ 0 ⟩ − i sin 2 ϕ ∣ 1 ⟩ ) The probability for measuring ∣ 0 ⟩ results to ⟨ 0 ∣ H ⋅ R ϕ ⋅ H ∣ 0 ⟩ = cos 2 2 ϕ = ! 4 3 ⇒ ϕ = 3 π