Question 13
Let be a curve passing through such that slope of normal at any point lying in the first quadrant is negative and the normal and tangent at any point cuts the -axis at and respectively such that the mid-point of is the origin, then find the number of solutions of and .
This question is part of the set For the JEE-nius;P .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Solution is really Long so here goes
1st Let us find the y-coordinates of the points of intersection of normal and tangent with Y-axis, Assuming a point P( x 1 , f ( x 1 ) )
Point of intersection of Normal is : y − f ( x 1 ) = f ′ ( x 1 ) − 1 ( 0 − x 1 ) , x-coordinate is 0
Point of intersection of tangent is : y − f ( x 1 ) = f ′ ( x 1 ) ( 0 − x 1 ) , x-coordinate is 0
As the midpoint of these 2 points is origin we add their y-coordinates and equate it to 0 to get a differential equation.
0 = 2 f ( x ) − x ( f ′ ( x ) − f ′ ( x ) 1 ) Also substituted ( x 1 , y 1 ) as ( x , y )
rearranging to get a quadratic, ( f ′ ( x ) ) 2 − 2 x y f ′ ( x ) − 1 = 0
taking its +ve root, writing f ′ ( x ) as d x d y ...(It is given that slope is +ve in 1st quadrant)
d x d y = 2 f r a c 2 y x + x 2 4 y 2 + 1
\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{y+\sqrt{y^2+x^2}{x}
Putting y = t x to solve this differential equation,
we get equation as t + 1 + t 2 = x c where c is constant of integration
resubstituting t = f r a c y x and rearranging,
y + x 2 + y 2 = x 2 c
Using (3,4) we find c as 1. Now solve the 2 equations any way you want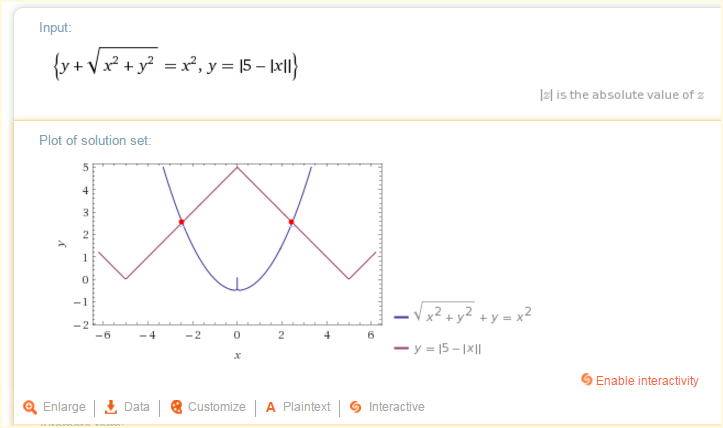
so answer is 2 solutions