Easy As A Sum, So Why The Product?
∫ 0 2 0 ( ⌊ x ⌋ { x } ) d x = ?
Details and assumptions :
-
Every x ∈ R can be written as x = ⌊ x ⌋ + { x } .
-
⌊ x ⌋ denotes greatest integer less than or equal to x .
-
{ x } is the fractional part of x .
The answer is 95.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
6 solutions
Wrong method .please do not make solutions like this. In this question we must use the concept of areas
Log in to reply
It is absolutely correct. Why is it necessary to use areas?
Log in to reply
And even that uses the concept of an integral, even if we don't it as such!
According to the definition of integral as Area below the curve , we can get the answer for this.
In the given range, the curve will be consisting of 1 9 triangles, something like as follows
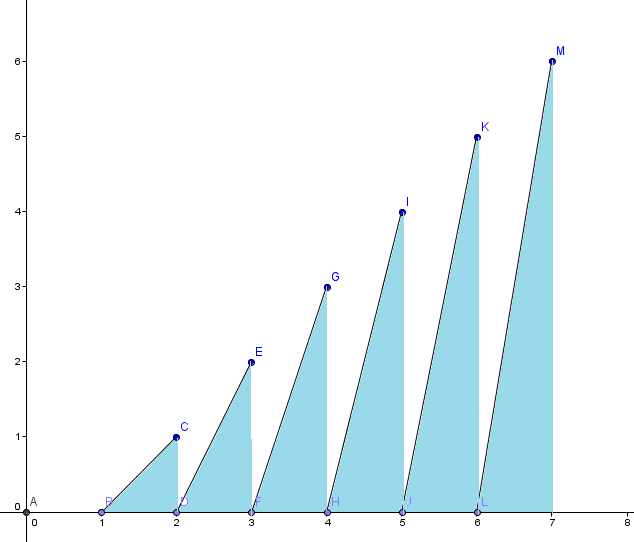
Areas of these triangles are in Arithmetic Progression,
as their bases are all 1 , but heights are 1 , 2 , 3 , . . . , 1 9 that means the areas are 2 1 , 2 2 , 2 3 , . . . , 2 1 9
Their sum would be 2 1 k = 0 ∑ 1 9 k = 2 1 2 1 9 ( 1 9 + 1 ) = 9 5
Very good concept
To Find ∫ N N + 1 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } d x
(where N is an integer)
Given x = ⌊ x ⌋ + { x } Squaring x 2 = ( ⌊ x ⌋ + { x } ) 2
x 2 = ⌊ x ⌋ 2 + { x } 2 + 2 ⌊ x ⌋ { x }
Integrating LHS & RHS in the limit N to N+1 L H S = R H S 1 + R H S 2 + 2 ∫ N N + 1 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } d x
L H S = ∫ N N + 1 x 2 d x = N 2 + N + 3 1 R H S 1 = ∫ N N + 1 ⌊ x ⌋ 2 d x = area of a rectangle with base 1 and height N 2 = N 2
R H S 2 = ∫ N N + 1 { x } 2 d x = ∫ 0 1 x 2 d x = 3 1
Hence ∫ N N + 1 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } d x = 2 N
Using the above result for a positive integer p,
∫ 0 p ⌊ x ⌋ { x } d x = 2 1 i = 0 ∑ p − 1 i = 4 p ( p − 1 )
Note: Sum of first n integers = 2 n ( n + 1 )
when p=20, answer = 95
Moderator note:
Great approach of relating ⌊ x ⌋ { x } to x 2 , which allows us to evaluate the integral.
I think a similar solution has be published. I'm too lazy to read it :)
Basically using x 2 = ( ⌊ x ⌋ + { x } ) 2 = ⌊ x ⌋ 2 + { x } 2 + 2 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } ∫ 0 2 0 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } = 2 1 ∫ 0 2 0 ( x 2 − ( ⌊ x ⌋ 2 + { x } 2 ) ) d x = 2 1 ( 3 2 0 3 − ( 6 1 9 ⋅ 2 0 ⋅ 3 9 + 3 1 × 2 0 ) ) = 9 5
Moderator note:
Great approach! Thanks for sharing it.
[x]{x}= x[x] - [x]^2 , integrating 1st part and 2nd part respectively we get 2565 and 2470 . so the ans is (2565-2470)=95
Hint-break integration in parts like from 1 to 2 then 2 to 3........ 19 to 20...... value of GIF will be constant for respective case like it will be 3 for 3 to 4.....and area of fractional part of x will be the same 1/2 which u can easily find by its graph
By using properties of definite integral and floor function.
∫ 0 2 0 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } d x = k = 0 ∑ 1 9 ∫ k k + 1 ⌊ x ⌋ { x } d x = k = 0 ∑ 1 9 ∫ k k + 1 k { x } d x = k = 0 ∑ 1 9 k ∫ 0 1 x d x = k = 0 ∑ 1 9 2 k = 9 5