Radicalised by the light
Consider the following radical equations:
W , Y and Z are radicals. The radical W radical can be thought of as an electron excess protonation of an anion: X
Y and X are dangerous species in biological systems. Y reacts with DNA. This reaction mutates DNA into a carcinogen: (P denotes the unchanged portion of the molecule)
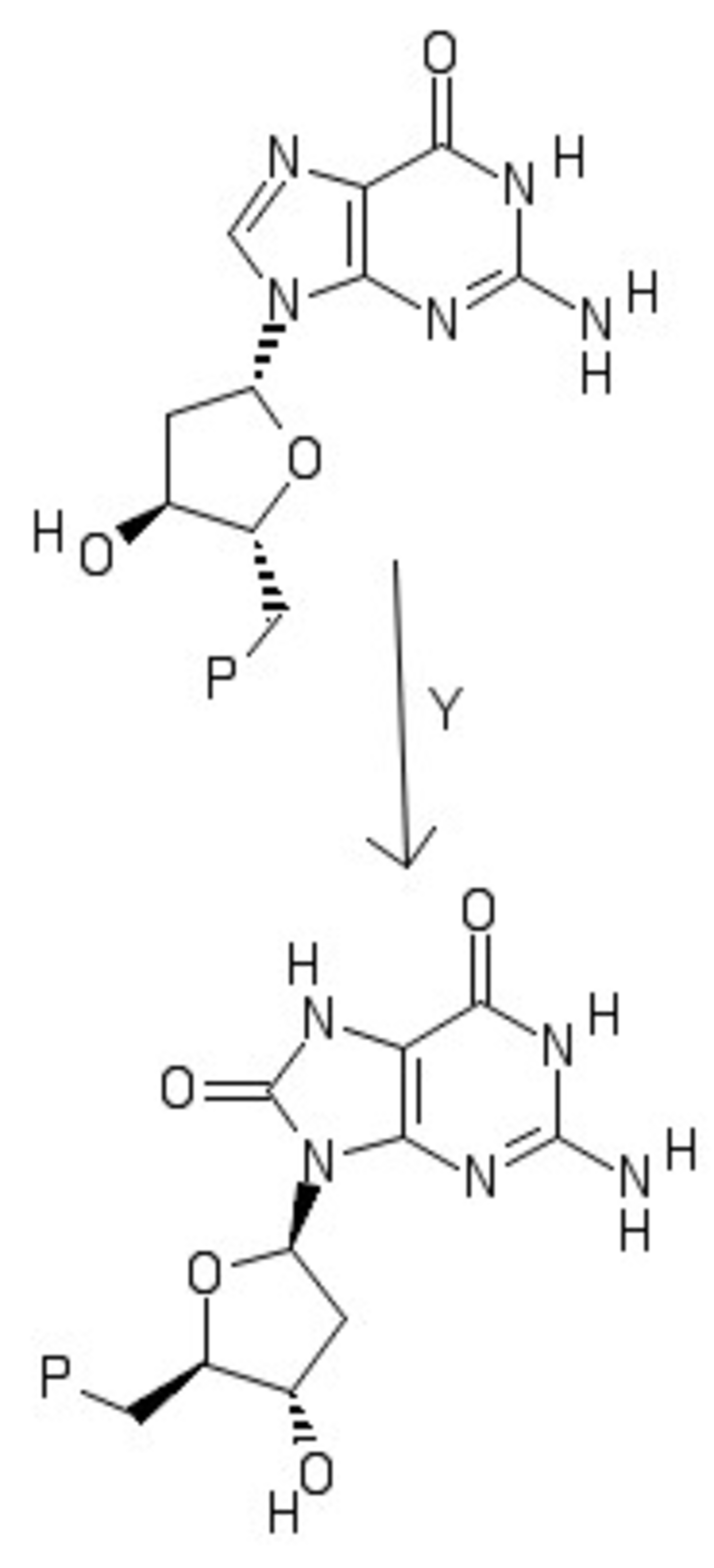
Aware of the dangers these species present, the body produces an enzyme M-S that converts these species into useful products. M is a d-metal and S is the enzyme substrate.
We denote and :
Without this enzyme, these species would accumulate in the cells which leads to autophagy resulting in cell death.
The hydrated isomer of D is used to treat cancer as it allows the radicals to accumulate in cancer cells resulting in their death but just like all medicine, "sola dosis facit venenum" .
Compound D is prepared through the following scheme: We start with the precursor E ,
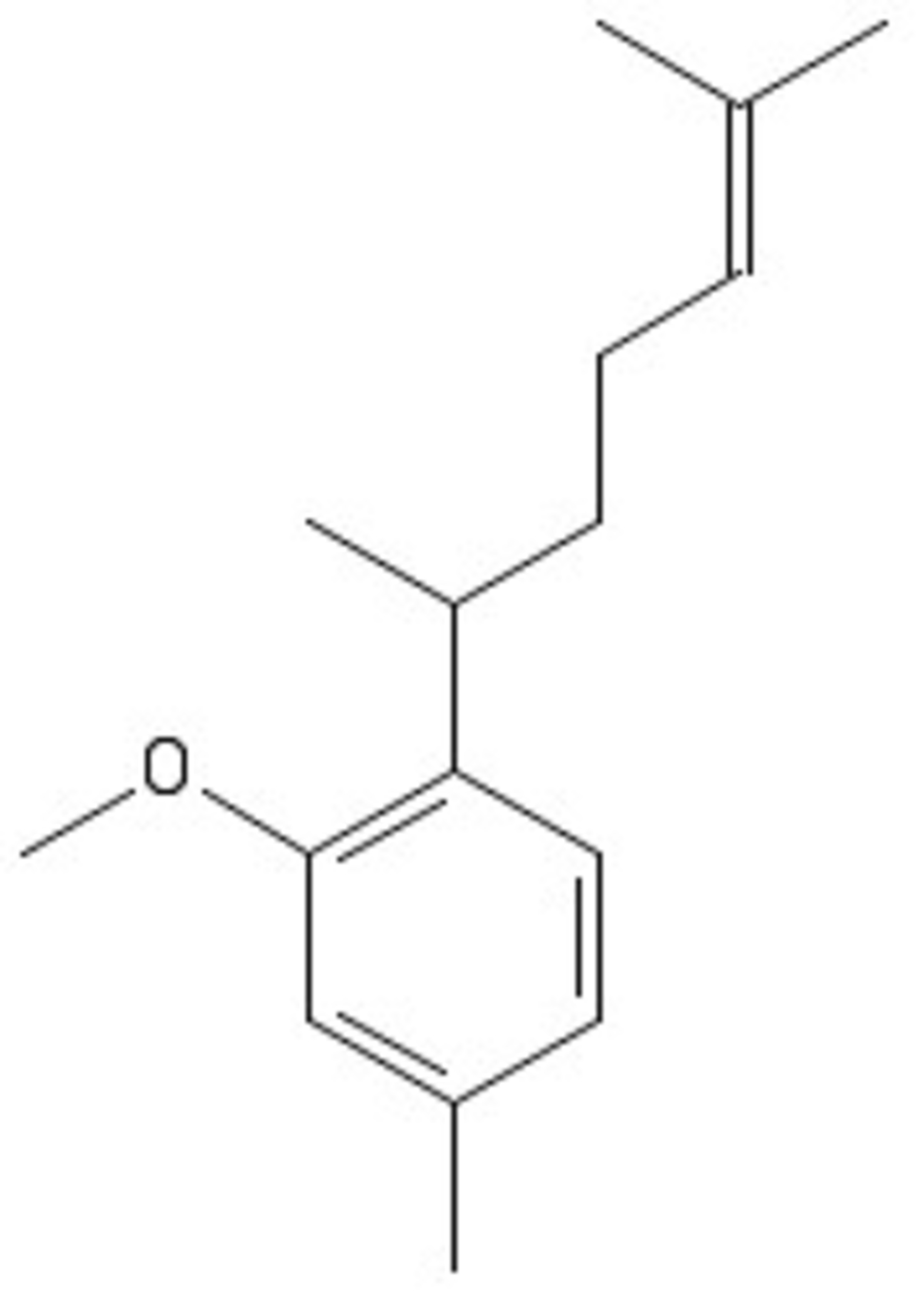
-
We expose it to light to form an equal amount of regio-isomers A and B .
-
In the presence of both regio-isomers form C
-
C reacts with and later is later heated with in a basic medium to form D whose formula is
If the mass of X is and the number of rings in A is ,
Calculate the value of
BONUS
-
Provide an electron pushing mechanism for DNA degradation.
-
Identify compounds U - Z .
-
Identify compounds A - D .
-
Provide an electron pushing mechanism for the transformation of E to A and B and explain why equal amounts are obtained.
The answer is 28.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
0 solutions
No explanations have been posted yet. Check back later!