Radius of the Circle O
A
B
and
B
C
are the two chords of circle
O
, and
A
O
is perpendicular to
B
C
.
A
B
=
3
,
B
C
=
2
2
, What is the radius of circle
O
?
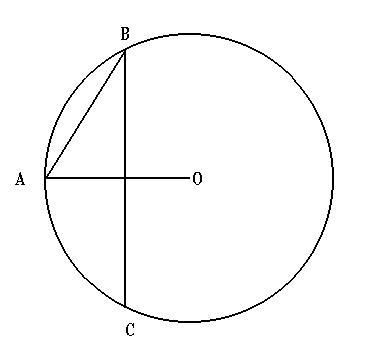
The answer is 1.5.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Extend A O ,and A O intersects the circle at D ,and A O intersects B C at E . A E = 1 , A B 2 = A E × A D = 3 , A D = 3 , A O = 1 . 5
Because AO is perpendicular to BC, AO is the perpendicular bisector of BC, therefore AB equals AC.A triangle with sides of 3 , 3 and 2 2 has, e.g., vertices at { { 0 , 0 } , { 2 2 , 0 } , { 2 , 1 } } . The circumcircle for these points has a center at { 2 , − 2 1 } with a radius of 2 3 . Perpendicular bisectors from AB and AC intersect at the center.
Let D be the intersection of B C and A O , and draw radius O B . Let r be the radius of circle O , so O B = O A = r .
Since A B = 3 and B D = 2 , by Pythagorean's Theorem on △ A D B A D = A B 2 − B D 2 = ( 3 ) 2 − ( 2 ) 2 = 1 .
This means that O D = A O − A D = r − 1 .
Then by Pythagorean's Theorem on △ B D O , D B 2 + D C 2 = B O 2 , or ( 2 ) 2 + ( r − 1 ) 2 = r 2 which solves to r = 1 . 5 .