Rectangle inscribed of circle
Level
1
A rectangle is inscribed inside a circle such that the area of the rectangle is half of the area of the circle. What is the ratio of the longer side of the rectangle to the shorter side?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let’s call the sides of the rectangles x and y and call the radius r . By our given information, twice the area of the rectangle is equal to the area of the circle. Our equation is: 2 x y = π r 2 Now we can use the Pythagorean Theorem for a second equation because we can form a right triangle with the sides of the triangle as legs and the diameter ( 2 r ) as the hypotenuse: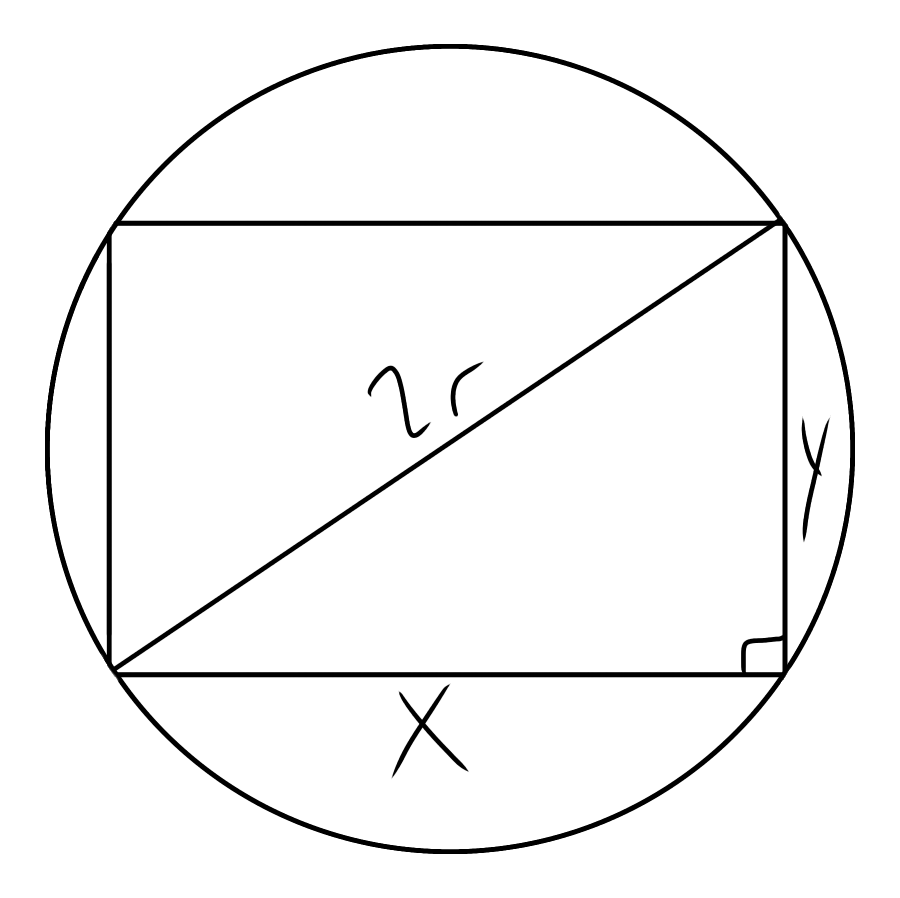 x
2
+
y
2
=
4
r
2
Our goal is to find what
y
x
is, so we can cancel out the
r
2
term by dividing our two equations by each other:
x
2
+
y
2
2
x
y
=
4
π
Cross multiply:
8
x
y
=
π
x
2
+
π
y
2
Move everything to one side:
π
x
2
−
8
x
y
+
π
y
2
=
0
At first, factoring this seems impossible. However, remember that we are looking for
y
x
. It would make this problem easier if we could turn our quadratic into one variable. In this case, since we are looking for
y
x
, we would want an equation in the form of
a
(
y
x
)
2
+
b
(
y
x
)
+
c
=
0
. This can be acheived by diving the equation by
y
2
:
π
(
y
x
)
2
−
8
(
y
x
)
+
π
=
0
To find what
y
x
is, we can use the quadratic formula:
y
x
=
2
π
8
±
2
1
6
−
π
2
Which simplifies to:
y
x
=
π
4
±
1
6
−
π
2
Now we have two answers. One of these answers is the one when
x
is the longer side (in which the answer is bigger) and one of them is when
x
is the shorter side (in which the answer is smaller). We choose the bigger value to find our answer:
π
4
+
1
6
−
π
2
x
2
+
y
2
=
4
r
2
Our goal is to find what
y
x
is, so we can cancel out the
r
2
term by dividing our two equations by each other:
x
2
+
y
2
2
x
y
=
4
π
Cross multiply:
8
x
y
=
π
x
2
+
π
y
2
Move everything to one side:
π
x
2
−
8
x
y
+
π
y
2
=
0
At first, factoring this seems impossible. However, remember that we are looking for
y
x
. It would make this problem easier if we could turn our quadratic into one variable. In this case, since we are looking for
y
x
, we would want an equation in the form of
a
(
y
x
)
2
+
b
(
y
x
)
+
c
=
0
. This can be acheived by diving the equation by
y
2
:
π
(
y
x
)
2
−
8
(
y
x
)
+
π
=
0
To find what
y
x
is, we can use the quadratic formula:
y
x
=
2
π
8
±
2
1
6
−
π
2
Which simplifies to:
y
x
=
π
4
±
1
6
−
π
2
Now we have two answers. One of these answers is the one when
x
is the longer side (in which the answer is bigger) and one of them is when
x
is the shorter side (in which the answer is smaller). We choose the bigger value to find our answer:
π
4
+
1
6
−
π
2